7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
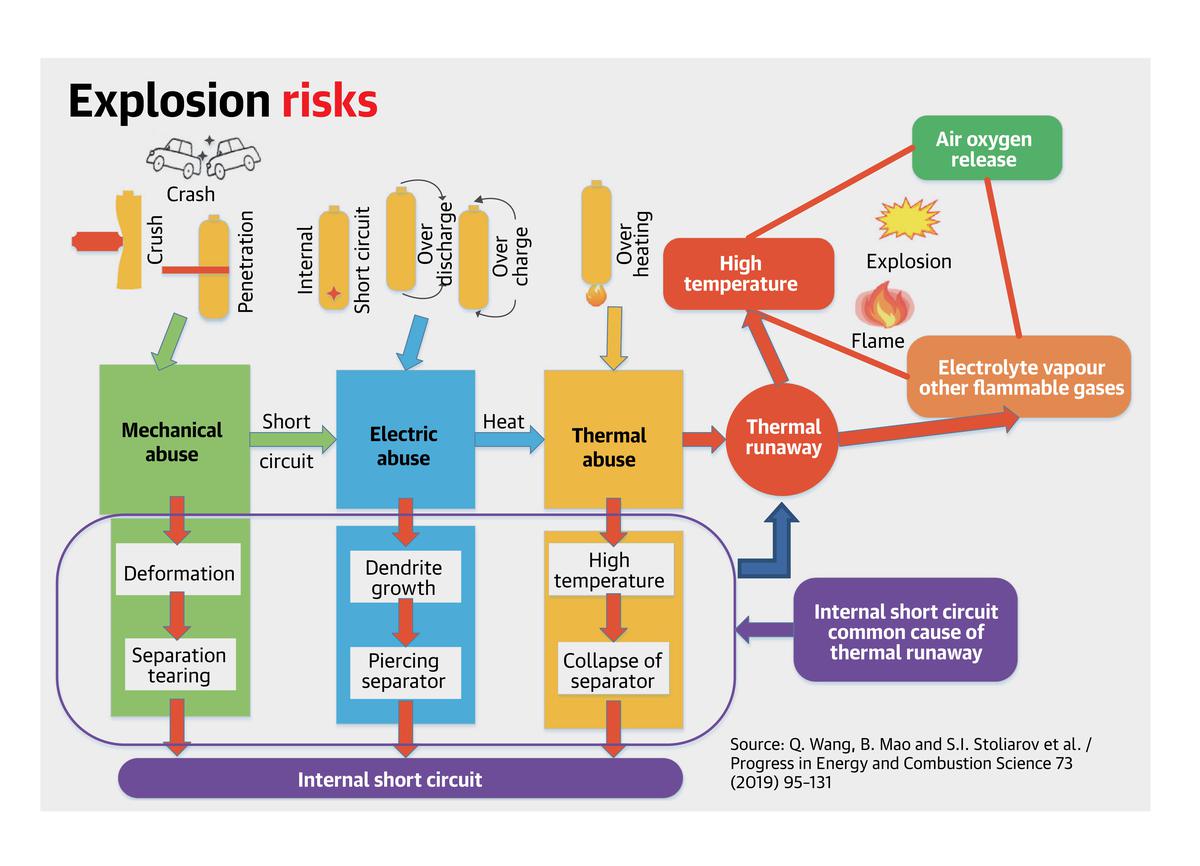
The Union Government has constituted an expert panel to probe the recent series of battery explosions in electric vehicles (EVs).
To know more about EV fires, click here
References