Mains: GS III - Science and Technology developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Recently, SpaceX partnered with Airtel and Jio to expand Starlink services across India.
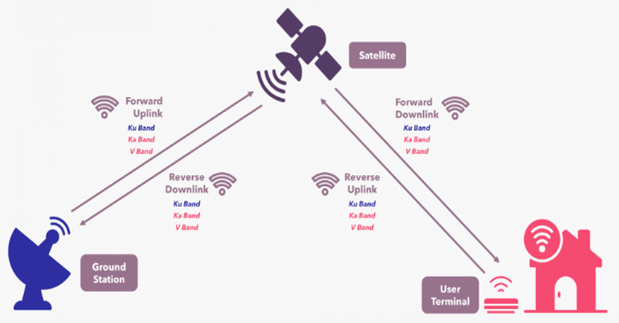
|
Satellite Constellation Project |
Owning Agency |
|
BlueBird satellites |
AST SpaceMobile. |
|
Starlink network |
SpaceX |
|
Project Kuiper |
Amazon |
|
OneWeb |
ISRO & Uk’s OneWeb Group |
NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) is a regional navigation satellite system of India, designed with a constellation of 7 satellites providing Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and Restricted Service (RS) for military purposes.
|
Starlink |
|
|
For Airtel and Jio |
Starlink allows them to provide high-speed Internet to India’s most remote regions without the infrastructure costs of terrestrial networks. |
|
For SpaceX |
It opens up a huge market in India. |
OneWeb, another constellation and closest competitor to starlink, operates fewer than 650 satellites, while Amazon’s Project Kuiper remains very small.
Tiered pricing models offer customers different levels of service or features at varying price points, allowing them to choose options that best suit their needs and budgets.
The Hindu| Partnership of Starlink with Airtel and Jio