7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) completed 10 years of its implementation.
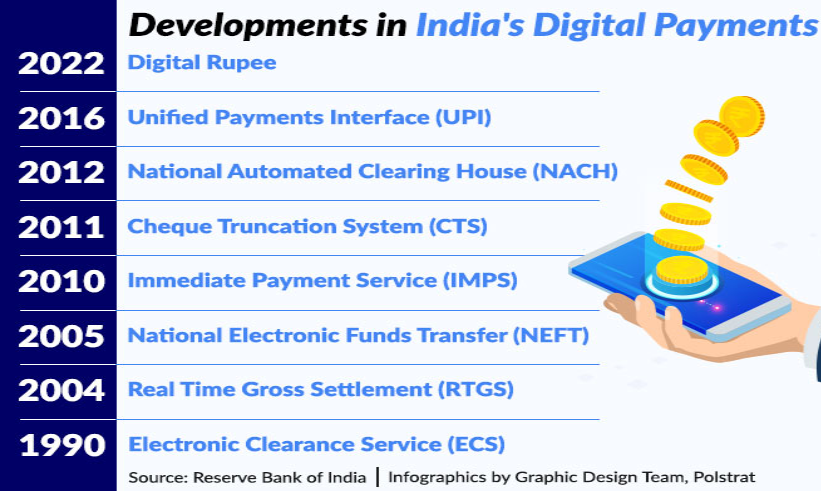
The JAM trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar and mobile) has enabled the government to shift to a more efficient system for transferring benefits directly to beneficiaries.
The government aims to open more than 3 crore new accounts under PMJDY during the financial year 2024-25.
Unified Lending Interface is a standardized, plug-and-play system that aims to reduce the need for extensive documentation from borrowers. It is designed to address unmet credit demand, particularly for agriculture and MSMEs by digitizing access to data like land records.
|
Other Financial Inclusion Initiatives in India |
|