7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
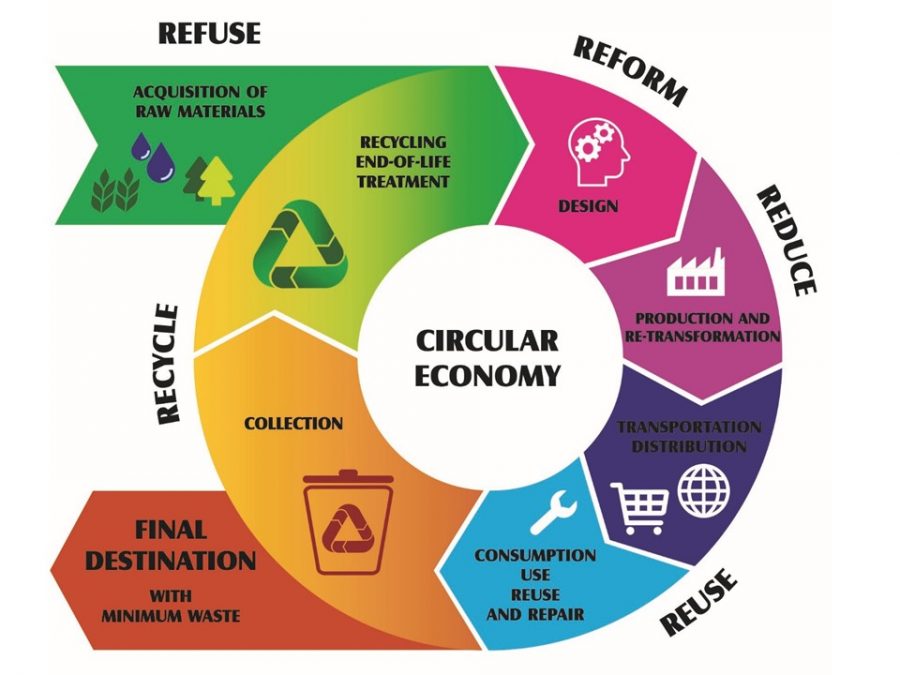
The COP27 meet brought to fore a circular economy’s relevance in mitigating carbon emissions by ensuring responsible consumption and sustainable resource management.
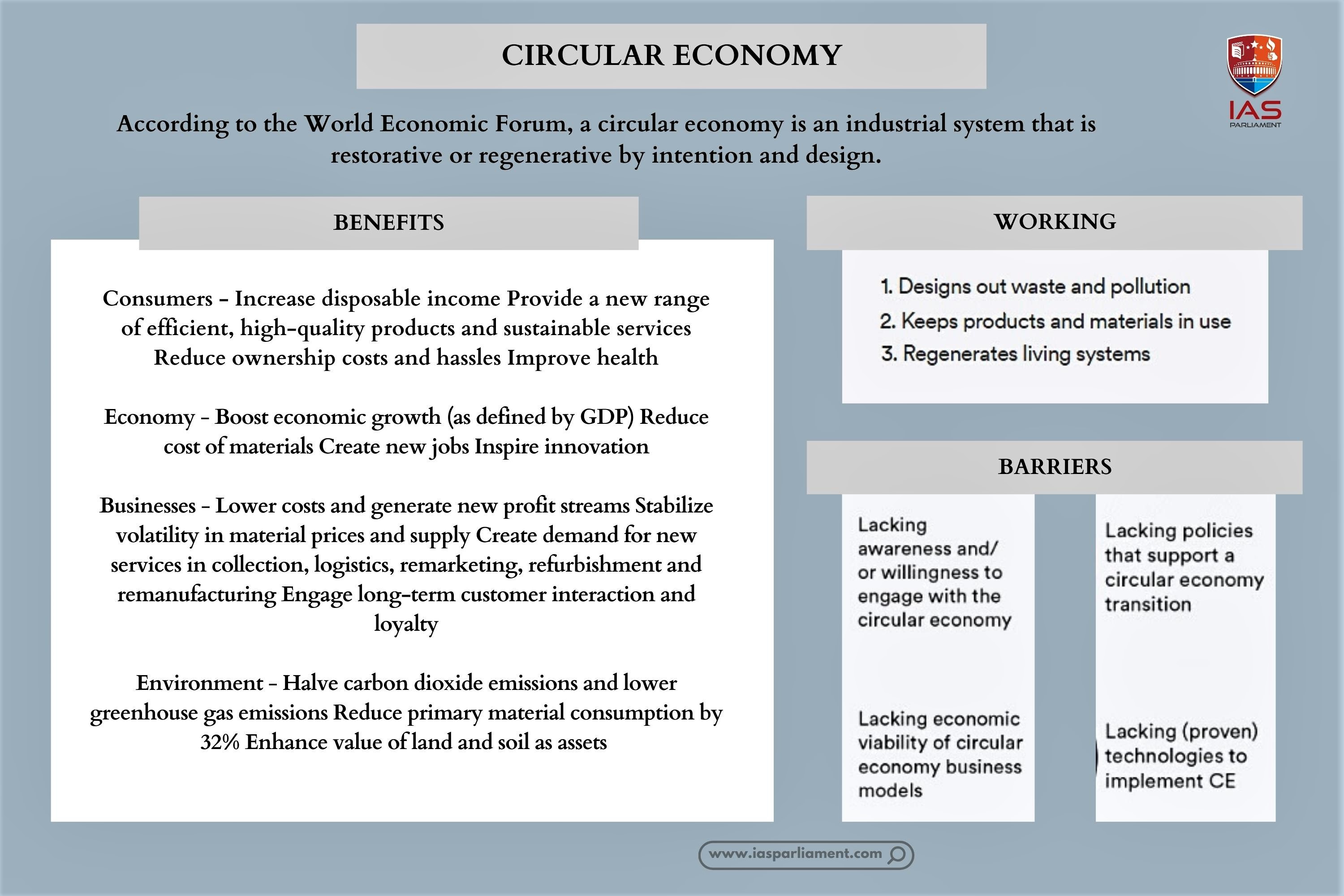 What are the challenges?
What are the challenges?
References