7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
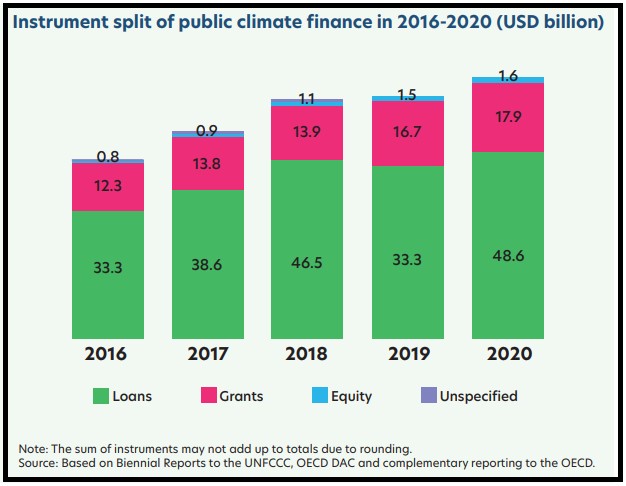
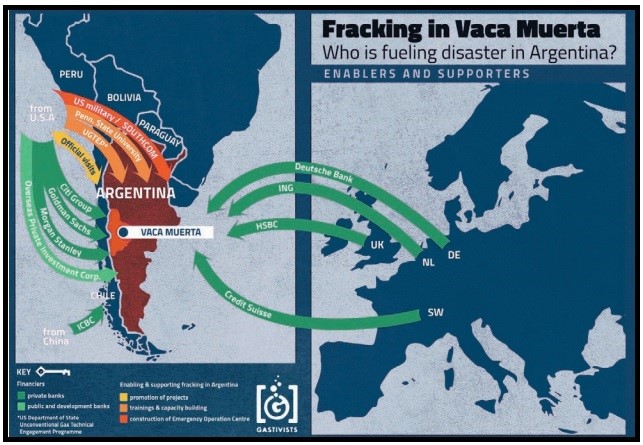
Debit-Fossil Fuel Trap report shows that Global North-imposed debt is locking the Global South into fossil fuels.