7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
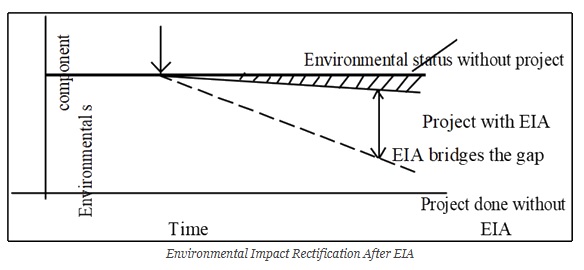
Recent Teesta dam breach in Sikkim and the flood and landslides in Himachal Pradesh are stark reminders for the need for a different set of environmental standards and clearances in Indian Himalayan Region.
|
Significance of Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) |
|
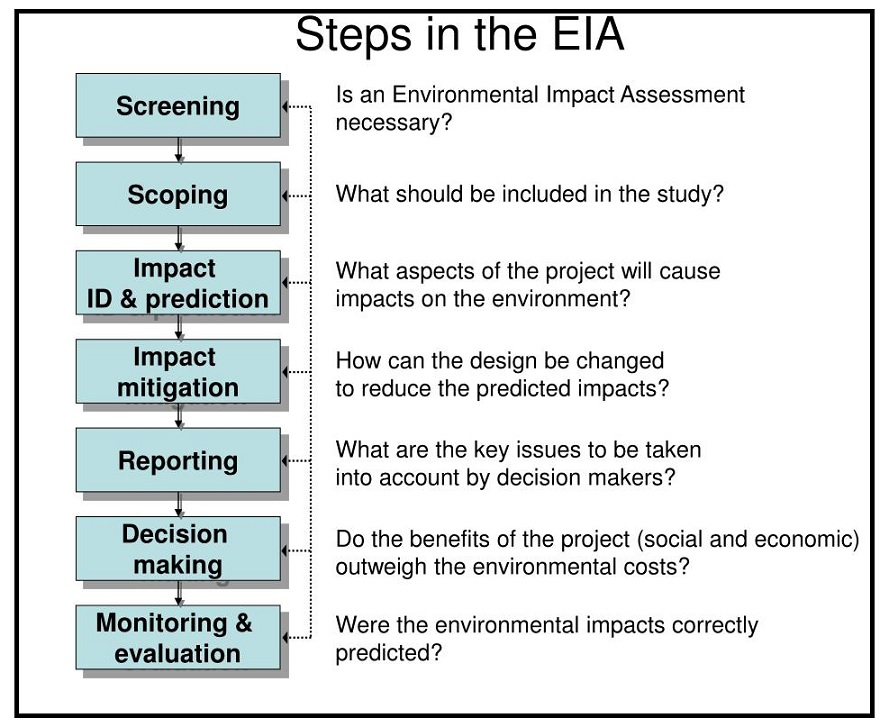
To know about the environmental clearance procedure, click here
References