7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
India lacks a targeted, comprehensive legal framework to combat lead poisoning with India experiencing alarming levels of exposure.
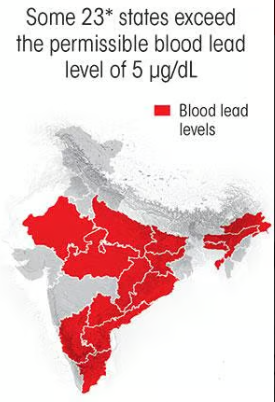
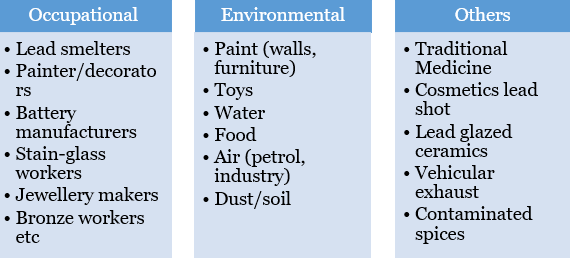
According to a 2020 report by the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) 275 million children in India record blood lead levels beyond the tolerable limit of 5 µg/dL.

India’s legal landscape includes nine pieces of primary legislation and nine pieces of subordinate legislation that touch upon various aspects of lead regulation.
Reference
The New Indian Express | Legal Framework to Combat Lead Poisonin