The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) has again cleared the proposal for commercial cultivation of genetically modified (GM) mustard.
A crop which has a gene artificially inserted into it from another species to give some desired properties (pest resistant, herbicide tolerant, etc.) is known as GM crop.
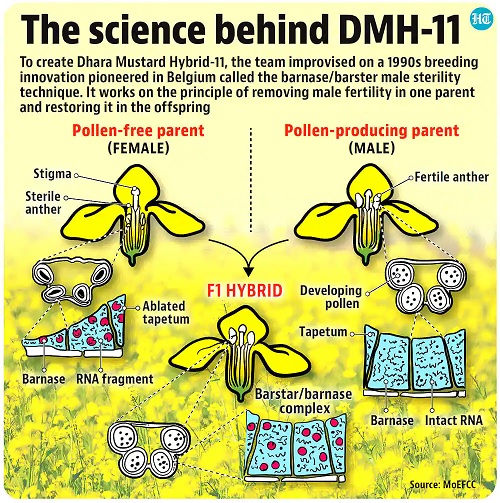
Hybridisation involves crossing two genetically dissimilar plant varieties that can even be from the same species. The first-generation (F1) offspring from such crosses tend to have higher yields than the parents.
India is the 4th largest contributor of oilseeds in the world and rapeseed and mustard contributes about 28.6% of total oilseeds production.
Pros of DMH-11
Cons of DMH-11
References
Quick facts
Mustard
Genetic engineering appraisal committee (GEAC)