Recently, Indian scientists have developed the first ever low-pungent mustard that is pest and disease-resistant.
India is the 4th largest oilseeds producer in the world. It has 20.8% of the total area under cultivation globally, accounting for 10% of global production.
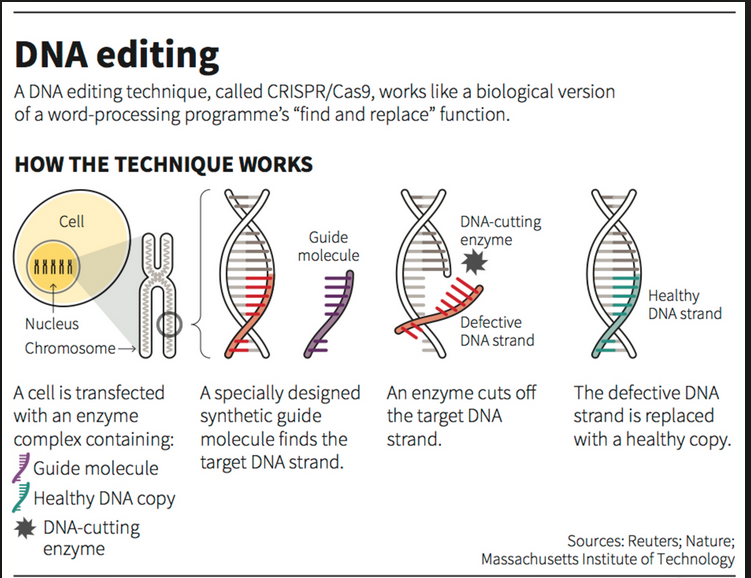
Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna in 2020 for their work in CRISPR/CAS9.
|
CRISPR Cas-9 |
|
|
About |
Genome modification |
Genome editing |
|
Definition |
Deliberate modification of the characteristics of an organism by manipulating its genetic |
Artificial alteration of the genetic material of an organism to produce desired characteristics |
|
Presence of Foreign DNA |
Involves introduction of foreign DNA |
Does not involve introduction of foreign DNA |
|
Procedure |
Targeted removal of desired genes |
Addition, removal and alteration of genetic material. |
|
Regulations |
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) gives the clearance. Union Government takes the final decision. |
Ministry of Environment exempted GE plants “free of exogenous introduced DNA” from the requirement of GEAC approval for open field trials leading to commercial release. |
|
Example |
Golden rice, Bt- Cotton, GM Mustard etc., |
Gene edited mustard |
Reference