7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
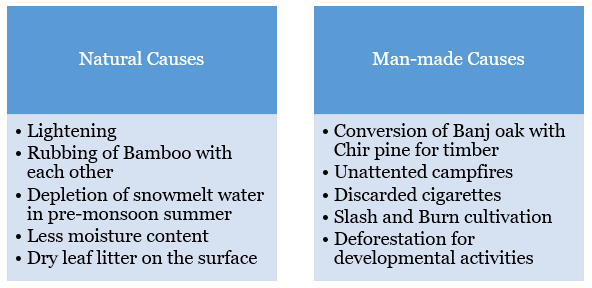
Recently, Himachal Pradesh (H.P.) is witnessing widespread forest fires across the region.
What is the status of forest fires in Himachal Pradesh?
Uttarakhand and Himachal, two of India’s Himalayan states, ranked first and second among states where most fire alerts had been sounded in 2023-2024.
To know more about Forest Fires in India, Click here
Himachal Pradesh is under Schedule V of the Indian Constitution, which requires community assent for development activities in the region. However, for large projects like hydro power generation, road widening, and four-lane highways, forests are being diverted with ease.

References