7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
Recently the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) has suggested that Union Government should not set aggressive targets for fiscal deficit.
|
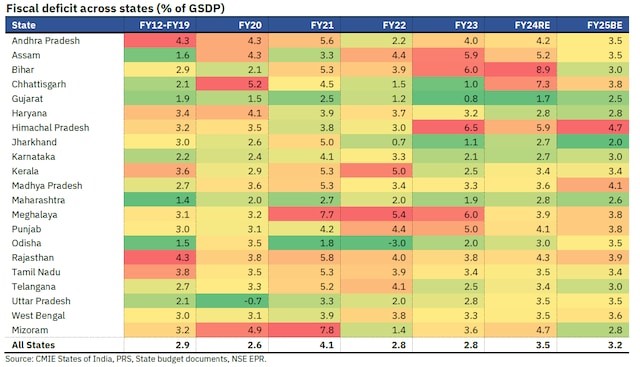
FRBM Act, 2003 |
|
What are the Constitutional provisions related to fiscal management?
|
Quick facts |
|
The Hindu | CII Urges Centre to Stick To Fiscal Deficit Target
Thomas Cook 3 months
Block Blast is supposed to be relaxing, right? Then why am I sweating like I’m defusing a bomb whenever the board is almost full?!