7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
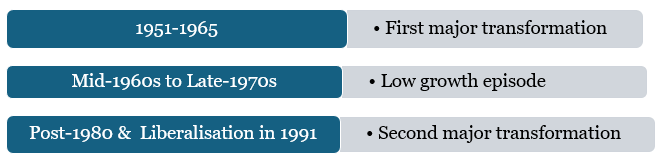
India's economic trajectory was defined by two key policy shifts: the planned development of 1951 and the liberalization of 1991, both catalyzing growth through distinct government roles.

Political acceptability comes more readily to a government visibly involved in supporting non-corporate private sector, reducing income inequalities and regional disparities, and addressing caste concerns