7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Mains (GS II & GS III) – Governance: Transparency & Accountability.
GS III – Environment and Conservation.
A recent poaching incident in Tamil Nadu’s Dharmapuri district has revived fears about illegal trade in wildlife products.
|
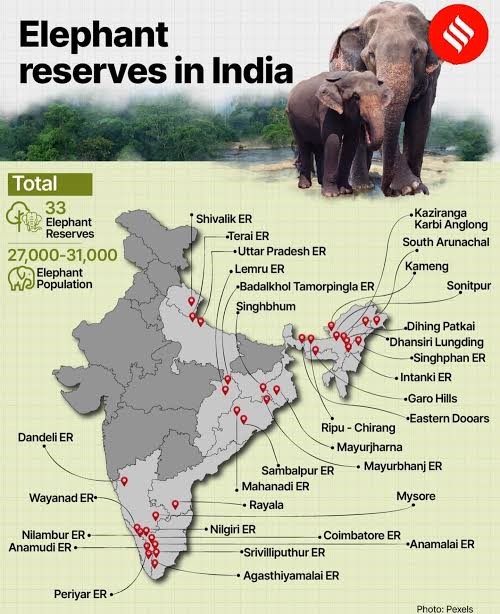
Distribution of Elephants |
|
References