7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The suo motu public interest litigation by the Meghalaya High Court very recently, to monitor the conservation of wetlands in the State brings the focus back on this important ecosystem.
Since 1971, February 2 is observed every year as ‘World Wetland Day’ to mark the adoption of the Ramsar Convention.
The theme this year 2025 was ‘Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future”.
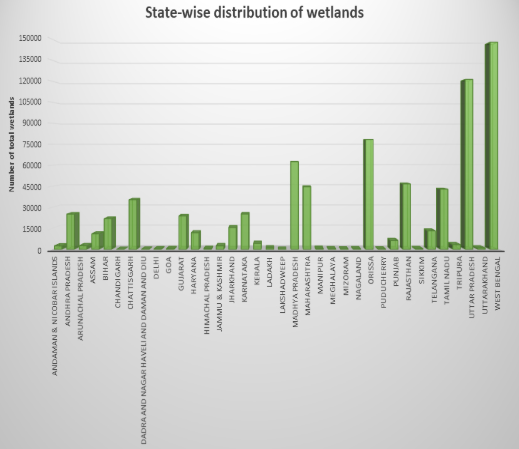
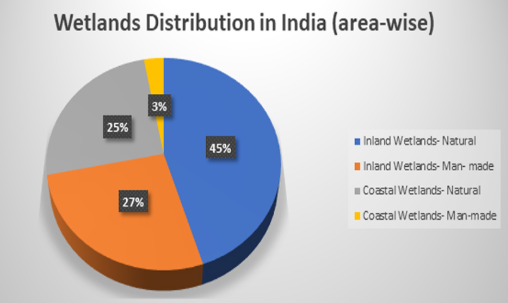
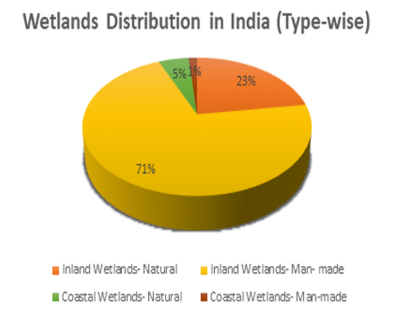
Ramsar Convention COP14 ,laid stress on preparation of the fifth Ramsar Strategic Plan and recognised that the conservation and management of wetlands cannot be a stand-alone initiative.
Click here for the mains practice question