7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
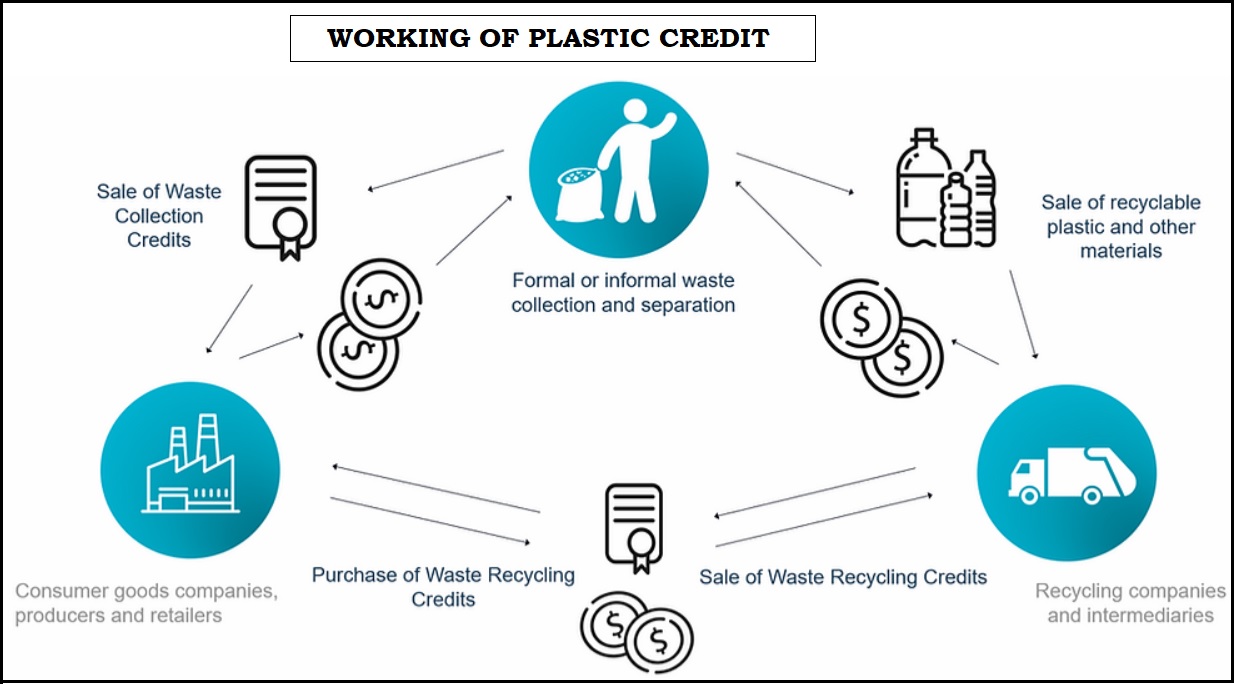
To cut down on plastic pollution, plastic credits are one of the tools being considered in UN-led talks in Nairobi.
References