7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
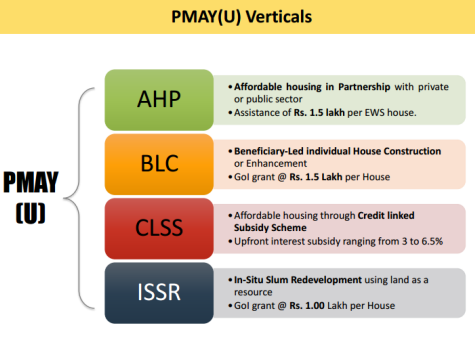
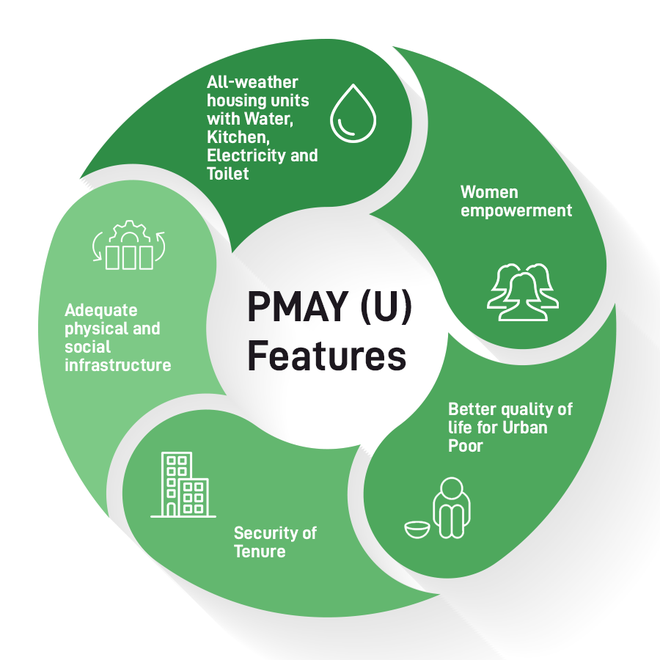
Recently, the Union cabinet approved for constructing 3 crore more rural and urban houses under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana with higher assistance per beneficiary.