7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
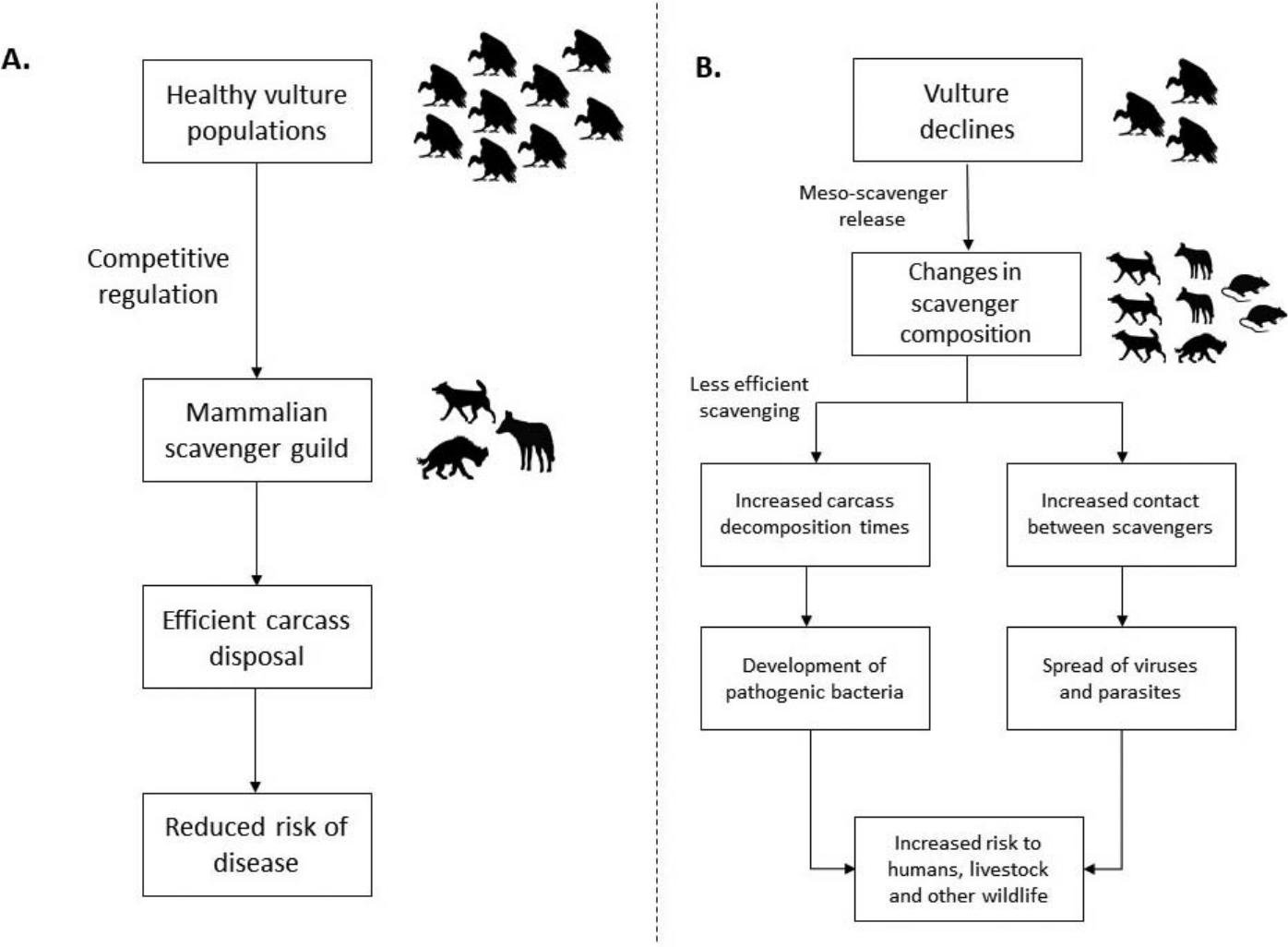
Recent study reveals that there is a strong link between Vulture decline in India and its impact on human health crisis.
Diclofenac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat sick cattle.
|
Conservation measures by India |
|