Christopher Nolan’s film “Oppenheimer” has ignited conversation around nuclear weapons.
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada, during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons.
Example- Nuclear fission of a uranium
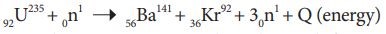
|
How the atom bomb works?
J. Robert Oppenheimer is called as the father of atom bomb.
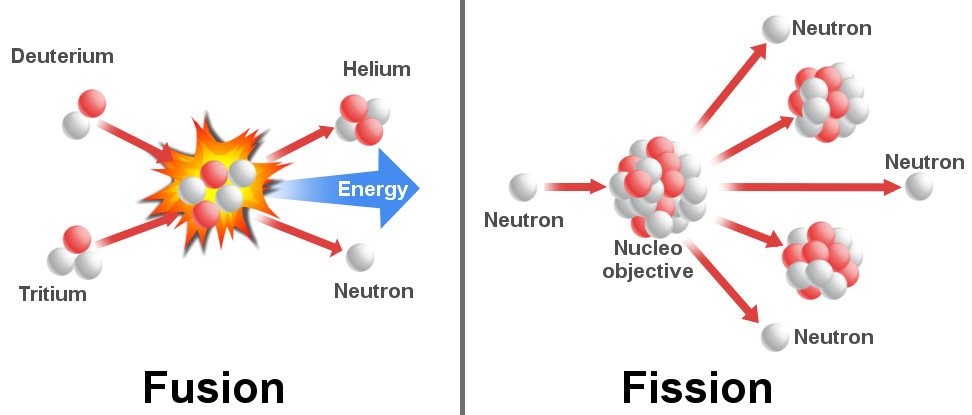
What is nuclear fusion?
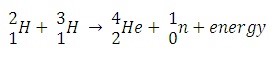
The energy released in a hydrogen bomb (or fusion bomb) is much higher than that released in an atom bomb
|
Features |
Nuclear Fusion |
Nuclear Fission |
|
About |
Lighter nuclei will join together to prouce heavy nucleus |
Heavy nucleus is divided into two fragments along with few neutrons |
|
Temperature |
Takes place at very high temperature (107 kelvin) |
Take place even at room temperature |
|
Conditions required |
High density and high temperature |
Critical mass of the substances and high speed neutrons |
|
Need of neutrons |
No need of external neutrons |
To start fission atleast one thermal neutron from outside is compulsory |
|
Energy |
Energy released per unit mass is high, nearly 7 times more than fission |
Energy released per unit mass is less |
|
Reaction |
No control on fusion reaction |
Can be controlled Example- Nuclear reactor |
|
Emissions |
Alpha rays, positrons, and neutrinos |
Alpha, beta and gamma radiations |
|
Example |
Hydrogen bomb |
Atomic bomb |
Reference