Why in News?
The new income tax bill, 2025 is expected to come into effect on 01 April 2026, will replace the existing Income Tax Act, 1961 (‘Act’).
Why in News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharman while presenting the Union Budget announced the launch of the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDKY).
The Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP), launched in 2018, aims to transform 112 under-developed districts across 28 states.
Cropping intensity is a measure of how efficiently land is used, and it is defined as the percentage of the gross cropped area to the net area sown.
At the all-India level, the cropping intensity was recorded at 155% in 2021-22, while the Cropping intensity was only 111% in 1950-51.
Why in News?
President Droupadi Murmu issued a proclamation under Article 356 to Manipur, citing a report from Governor Ajay Kumar Bhalla, addressing the ongoing issue of ethnic violence.

President's Rule has been imposed 134 times throughout 29 states and territories since 1950 when the Constitution first came into force, most frequently in Manipur and Uttar Pradesh 10 times each.
Why in News?
Union Health Minister launched National Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign for the elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) across 13 identified LF endemic states.
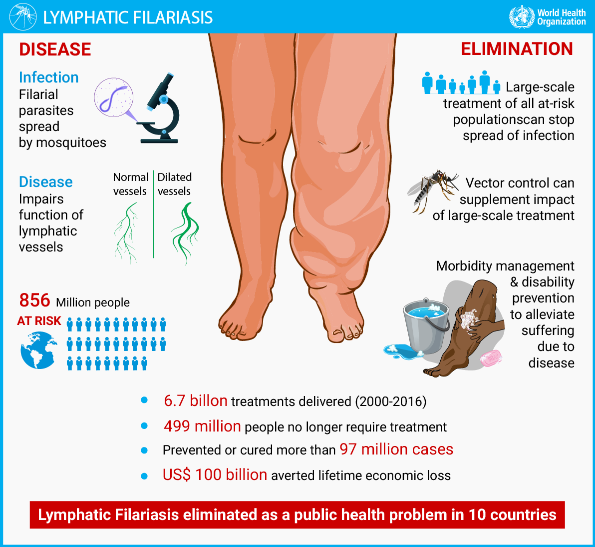
Mass Drug Administration (MDA) involves administering an annual dose of medicines to the entire at-risk population.
|
Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Campaign in India |
|
|
One Liners 15-02-2025 |
|
Polity & Governance |
|
Rashtriya Bal Swasthaya Karyakram (RBSK) 5.64 crore children have been provided secondary/tertiary care from 2014-2024 under RBSK.
|
|
Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (SASCI) Scheme Government sanctioned 40 projects in 23 States under SASCI Scheme
|
|
Sampoorna Bima Gram (SBG) Yojana
|
|
National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020
|
|
Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles in India (FAME India) FAME Phase-II was implemented for a period of 5 years from 2019-2024.
|
|
PM e-Bus Sewa-Payment Security Mechanism (PSM) Scheme
|
|
Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electric Passenger Cars in India (SPMEPCI)
|
|
Elephant Route Predictor App Elephant Route Predictor App will soon be launched on a pilot basis in Hazaribagh, Jharkhand.
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF)
|