7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
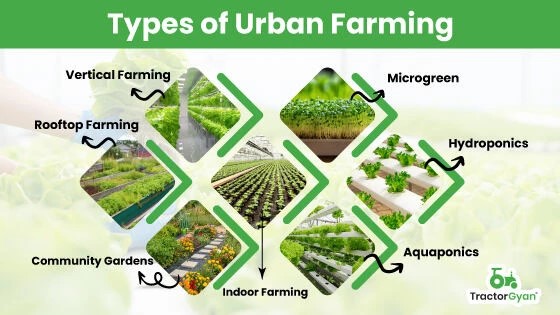
Urban farming, powered by Agriculture 4.0, is ushering in a new era of food production by integrating advanced technologies.