7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
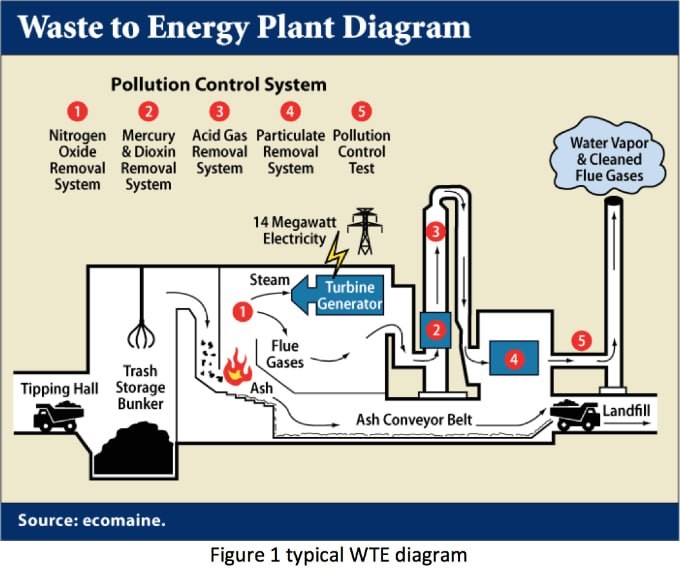
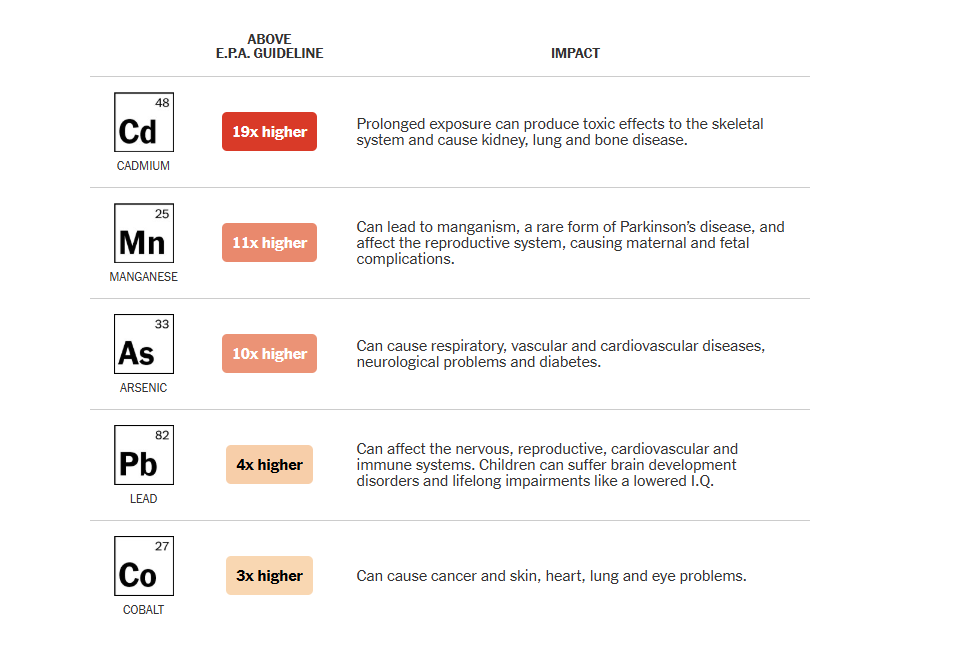
A recent investigative report by the New York Times on Delhi’s Waste-To-Energy (WTE) incinerators, said that it makes more harm than its benefits.
|
Status of waste to energy incineration plants in India |
|
Reference