7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
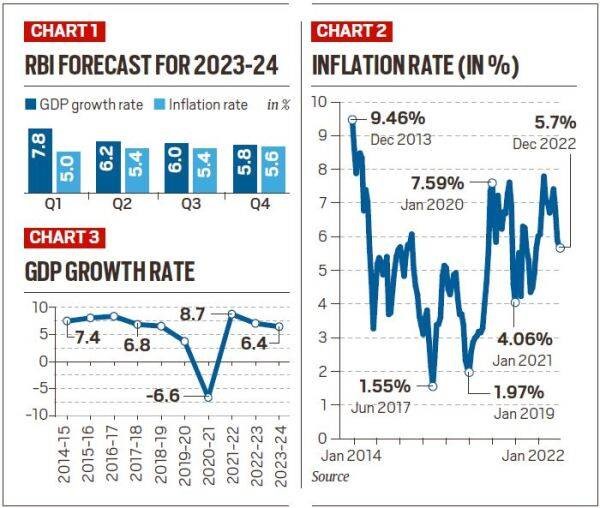
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) hikes repo rate by 25 basis points (bps) to 6.5% and has also projected a GDP growth for the next fiscal at 6.4%.
Quick facts
References