7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
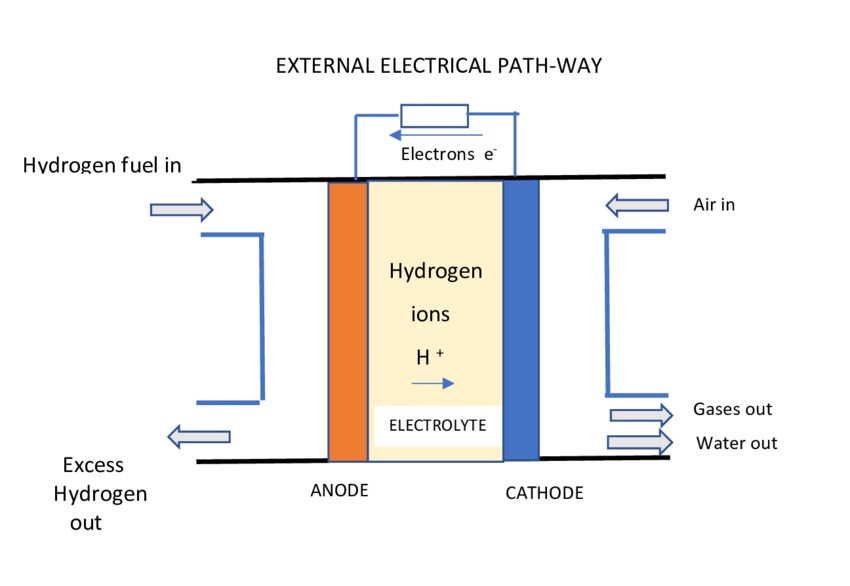
Hydrogen fuel cell technology is emerging globally as a valuable multisector alternative for fossil fuels.
References