7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in the news?
The Prime Minister, Narendra Modi while addressing the 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas convention stated that “today’s India not only firmly asserts its own point but also strongly amplifies the voice of the Global South”.
What is Global North-South divide?
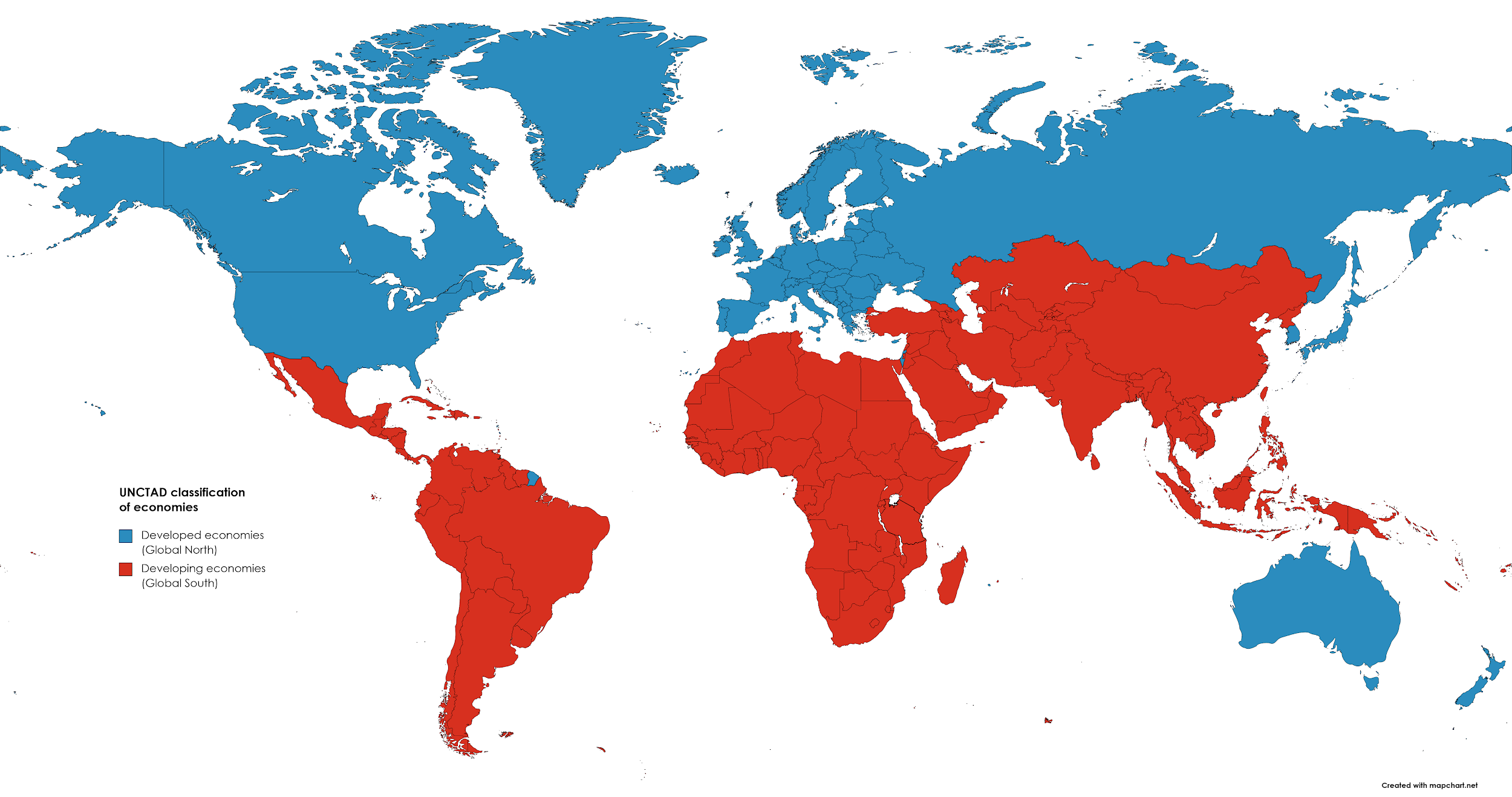
What are the Current Issues that Widen the Divide?
India aims to be the voice of the Global South and Focus on economic challenges, debt, and global influence while strengthening diplomatic ties with both blocs.
What is India’s Role in Bridging the Divide?
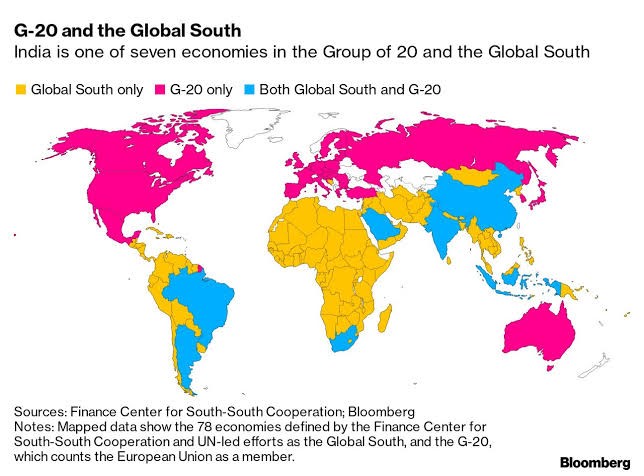
Geopolitical Leadership
Climate & Energy Leadership
What are the Challenges in India’s Role?
To Solve Mains question – Click Here
Reference
The Hindu - India as a Global North-South Bridge