7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
India-European Free Trade Association has signed a Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA).

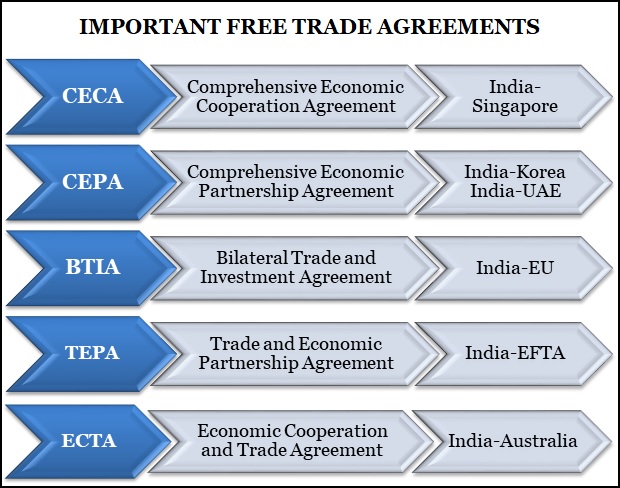
India runs a trade deficit with most of its top trade partners, except for the US. India also runs a trade deficit with EFTA at USD 14.8 billion in the last fiscal.
Highlights of TEPA
|
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) |
|
For EFTA Countries
For India
References