India joined the elite critical minerals club, Mineral Security Partnership to secure critical mineral supply chains.
Only about 10-20% of India’s critical minerals has been explored.
Australia produces almost half of the world’s lithium, is the second-largest producer of cobalt and the fourth-largest producer of rare earths elements.
Critical minerals - A critical mineral is a metallic or non-metallic element that is essential for the functioning of our modern technologies, economies or national security and there is a risk that its supply chains could be disrupted.
Rare earth minerals – Rare earth minerals comprises 17 elements which are classified as light RE elements (LREE) and heavy RE elements (HREE).
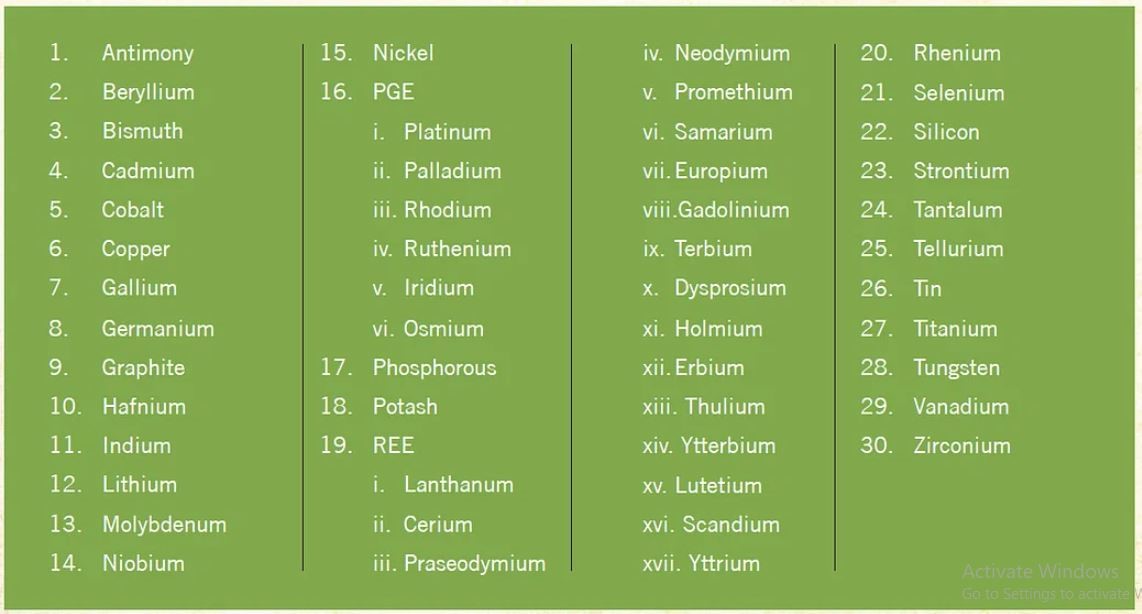
Critical Mineral List (30)