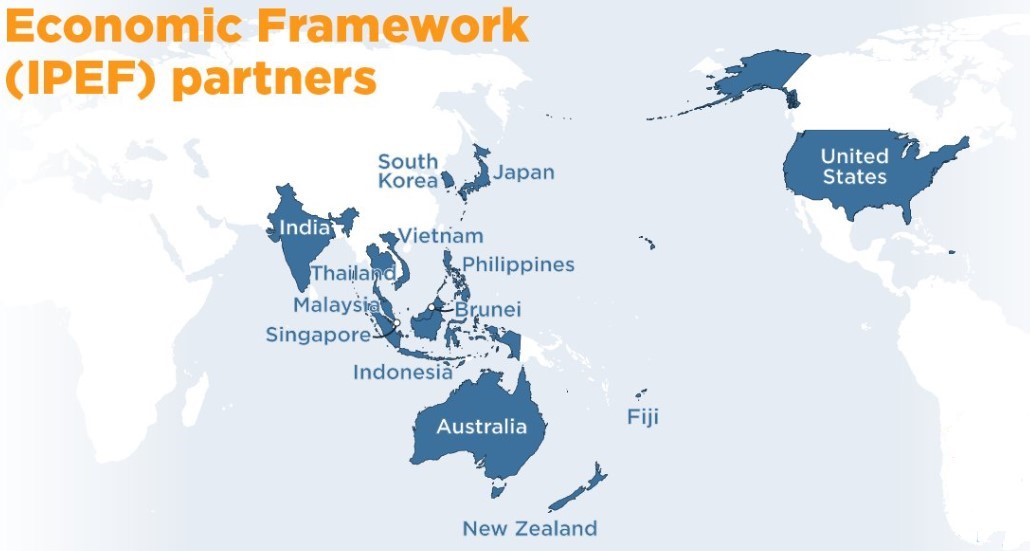
Recently India signed the US-led 14-member Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) bloc’s agreements on a clean and fair economy.
IPEF with its 14 partner countries represents 40% of global GDP and 28% of global goods and services trade.
|
IPEF Agreements |
Date of Entry into Force |
|
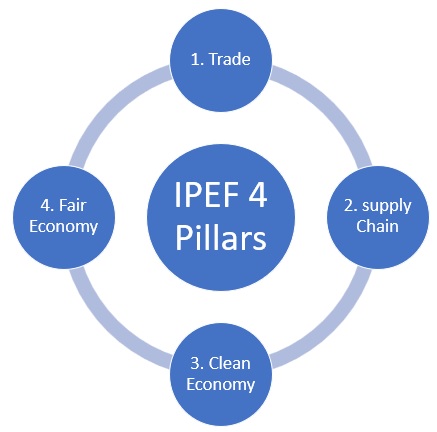
Supply Chain Agreement |
February 24, 2024 |
|
Clean Economy Agreement |
October 11, 2024 |
|
Fair Economy Agreement |
October 12, 2024 |
|
Overarching Agreement on IPEF |
October 11, 2024 |
India’s merchandise exports to the U.S. have risen by over 50% (54.4%) from $54.3 billion in 2018 to $83.8 billion, as reported in 2023.
|
Initiatives under IPEF |
|
|
IPEF Upskilling Initiative |
Providing digital skills training to primarily women and girls in IPEF emerging and middle-income partner countries. |
|
Critical Mineral Dialogue |
Strengthening the critical mineral supply chain and ensuring sustainable mining practices in the region. |
|
Tech Council |
Coordination and cooperation on key technologies like Cyber Security, Undersea Cables and Artificial Intelligence. |
|
Cooperative Work Program |
Facilitate collaborative and cooperative efforts among the interested participating IPEF countries to advance the objectives of the Clean Economy Agreement. |
India was elected as Vice Chair of the Supply Chain Council with US as Chair.
Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) facilitated duty-free access to more mature markets and it was withdrawn in 2019.
References