7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
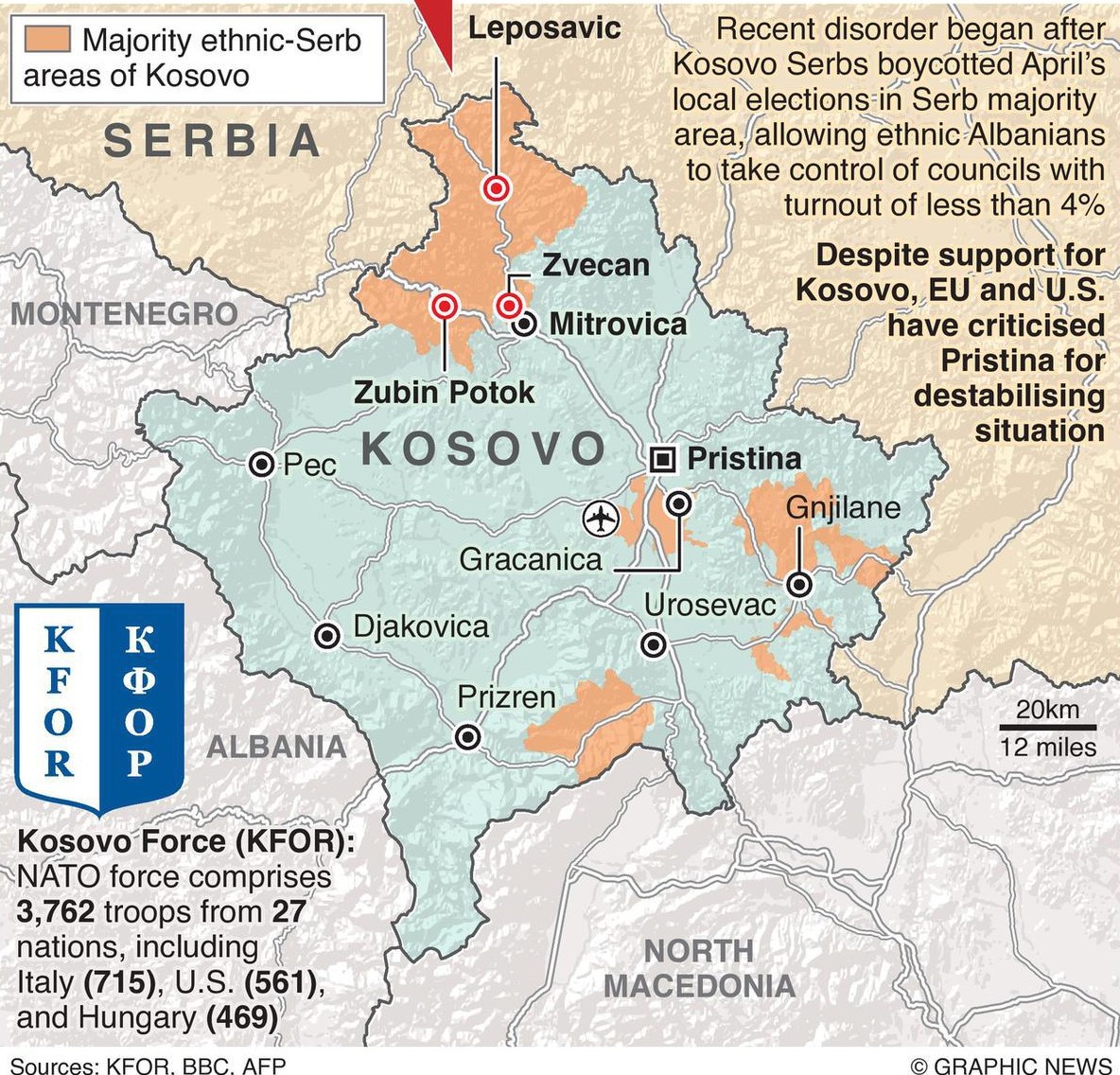
The tensions between Kosovo and Serbia escalates and clashes broke out between Serbs protesting in North Kosovo and the NATO-led Kosovo Force (KFor).
References
The Hindu | What is the Kosovo-Serbia conflict all about?