7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
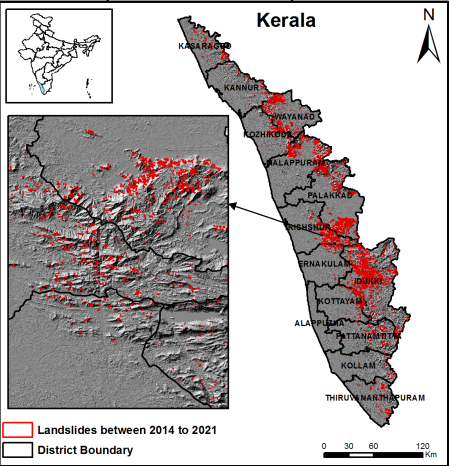
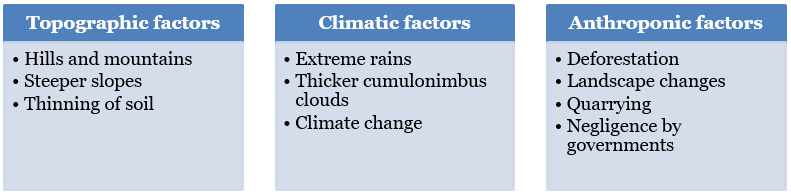
The death toll from the Wayanad landslides crossed 400 and around 152 people are still missing.