7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
What is the recent finding?
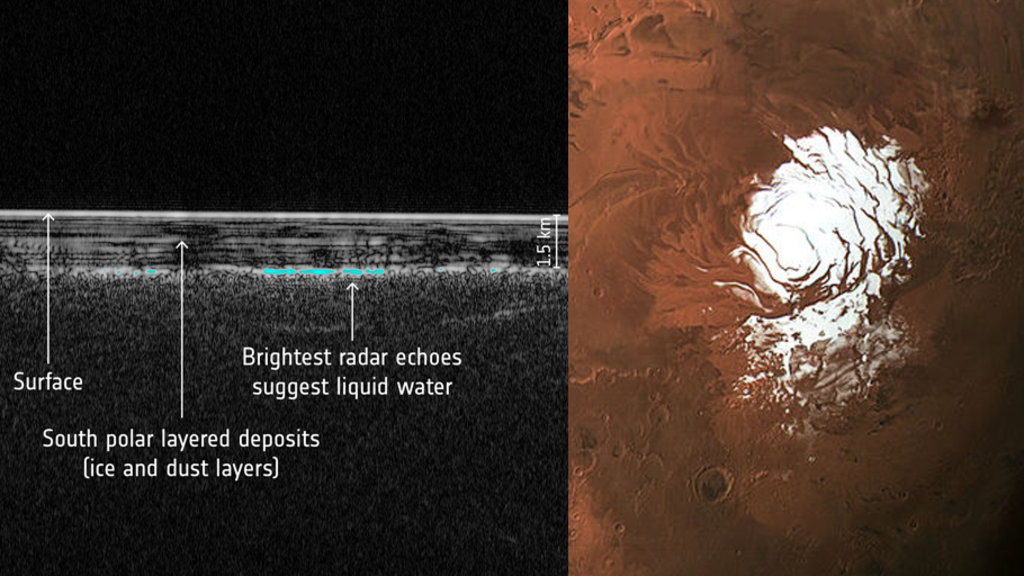
How in liquid form?
What is the significance?
Source: Indian Express, NewAtlas