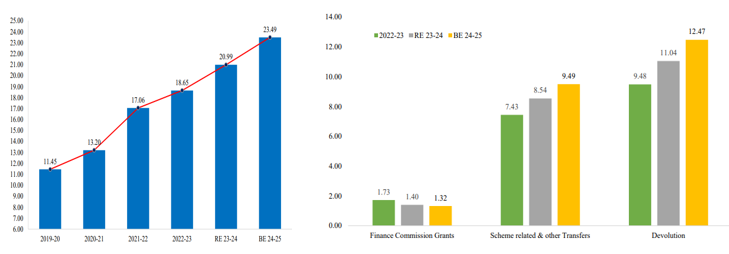
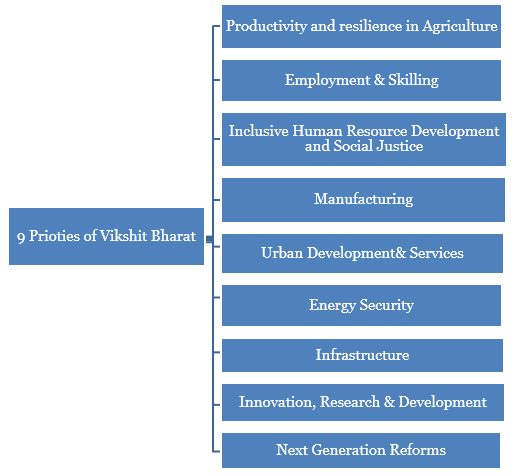
Key Highlights

Brownfield is the previously-developed land that has been abandoned or underutilized.
Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) is a regulatory instrument to reduce Specific Energy Consumption in energy intensive industries, to enhance the cost effectiveness through certification of excess energy saving which can be traded.
Vishwa Shanti Stupa is a large white Peace Pagoda in Rajgir, Nalanda District, Bihar. Rajgir is significant for being the holy place for Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.
Shram suvidha, launched in 2014, a platform for sharing of information among the labour enforcement agencies.
SAMADHAN is Software Application for Monitoring, Disposal and Handling of Industrial Disputes.
National Pension Scheme (NPS) is a voluntary pension system for all citizens, including both residents and NRIs between the ages of 18 and 70 years.
Variable Capital Company is a new corporate structure introduced in Singapore in January 2020 to meet corporate financial needs.
References