Why in news?
Indian authorities have arrested six individuals in Jharkhand for allegedly being involved in illegal online trading of wildlife parts, including a substance called Hatha Jodi.
What is illegal wildlife trade?
- Illegal wildlife trade- It refers to the illegal buying, selling, or exchange of wild animals, plants, and their derivatives.
- It includes the trafficking of endangered species protected by law and the trade of wildlife products without proper permits or in violation of national and international regulations.
- Types of illegal wildlife trade
o Live animals and plants- Trafficking of live specimens for pets, zoos, or private collections.
o Animal parts- Trade in products like ivory, rhino horn, pangolin scales, and tiger skins.
o Plants and plant products- Illegal trade in timber, medicinal plants, and rare flora.
- Magnitude of illegal wildlife trade- Between $7 and $23 billion per year globally.
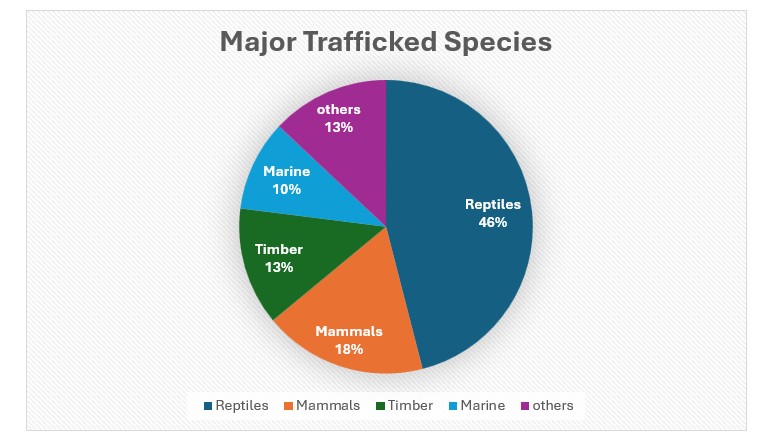
- Top countries of wildlife trafficking

|
Hatha Jodi
|
- Hatha Jodi is the hemipenis of the monitor lizard (Varanus spp),
- It is illicitly obtained and falsely marketed as a sacred charm or root with mystical properties.
- Monitor lizards are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972.

|
|
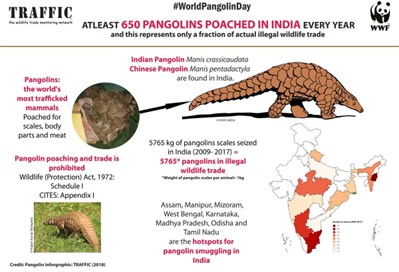
Pangolin Trafficking
|
|
|
What are the causes of illegal wildlife trade?
- Demand for Luxury goods - Items like ivory, rhino horns, and tiger skins are seen as status symbols in some cultures.
- Use in Traditional medicine- Certain wildlife parts are believed to have medicinal properties, driving demand in traditional medicine markets.
- Exotic pets- The demand for rare and exotic pets leads to the capture and trade of wild animals.
- Use as food - Pangolins are trafficked mostly due to demand for meat and scales.
- High profit margins- The illegal wildlife trade is a lucrative business with high profits, especially for rare species.
- Inadequate legal frameworks- Some countries lack strong laws or penalties to deter illegal wildlife trade.
- Border control challenges- Poorly managed borders make it easier for smugglers to transport illegal wildlife products.
- Superstitions and Demand - Belief among people that some animal parts like Hatha Jodi have magical powers in solving financial and health issues.
- Lack of awareness – Most of the perpetrators do not understand the gravity and impact of the crime.
What are the emerging challenges in controlling illegal wildlife trade?
- Social Media – Social Media is increasingly being used to propagate false information about wildlife products.
- This fuels the thriving illegal market for endangered animals.
- Encrypted communication - Privacy protection features such as encrypted chat and private social media groups further add challenges to tracing the illegal wildlife trade.
- New trade channels – Unregulated cyberspace channels and E-Commerce platforms being used for selling wildlife products pose new challenges to identifying and preventing wildlife crimes.
- Air Ports – Airports in India are major conduits for trafficking wildlife contraband.
- New methods of evading checks – New methods are used for evading the enforcement agencies in hiding articles through checked luggage and personal baggage.
- Wrong declaration of protected species.
What are the impacts of illegal wildlife trade?
- Species decline- Illegal trade often targets endangered species, pushing them closer to extinction.
- Ecosystem disruption- Removal of key species can disrupt ecosystem function and harm other wildlife.
- Tourism impact- Loss of wildlife can reduce ecotourism revenue, which many local economies depend on.
- Economic costs- Management and enforcement against illegal trade can be costly for governments.
- Organized crime- Wildlife trafficking is often linked to other forms of organized crime , corruption and terrorism.
- Local communities- Indigenous and local communities may lose traditional livelihoods tied to wildlife.
- Disease transmission- Illegal wildlife trade can spread zoonotic diseases (diseases transmitted from animals to humans).
What are the regulations in India?
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972- It provides for the establishment of wildlife sanctuaries and national parks and imposes penalties for illegal trade.
o Hunting or trading parts of Schedule I species under WPA act can result in imprisonment for 3 to 7 years and a minimum fine of Rs 25,000.
To know more about WPA act , Click Here.
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora)- India is a signatory to CITES, which regulates international trade in endangered species.
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)- Responsible for tackling wildlife crime across the country.
- Forest departments- Local Forest departments play a key role in monitoring and enforcement at the ground level.
- Project Tiger and Project Elephant- Government programs focused on conserving tiger and elephant populations.
- Protected Areas Network- A system of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries to safeguard habitats and wildlife.
- Awareness campaigns- Various NGOs and government bodies conduct campaigns to educate the public about the impacts of illegal wildlife trade and the importance of conservation.
- Cross-Border efforts- Collaboration with neighboring countries and international organizations to combat wildlife trafficking.
o TRAFFIC - Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network to monitor the international trade in wild plants and animals.
What lies ahead?
- Updating laws- Ensure that wildlife protection laws are comprehensive and adapt to emerging threats and new trafficking methods.
- Harmonizing regulations- Align national laws with international agreements like CITES to create a unified approach to wildlife protection.
- Training and capacity building- Provide training for law enforcement and customs officials on wildlife trafficking detection and investigation.
- Cross-Border collaboration- Foster collaboration between countries and international organizations to tackle the global nature of wildlife trafficking.
- Information sharing- Create networks for sharing intelligence and best practices among nations.
- Public awareness campaigns- Implement global and local awareness campaigns to educate the public about the impacts of wildlife trafficking and the importance of conservation.
- Advanced monitoring- Use technology such as drones, satellite imagery, and genetic tools to monitor wildlife populations and detect illegal activities.
- Data management- Develop robust data systems for tracking wildlife trade and enforcement actions to enhance analysis and response.
- Scientific research- Support research on wildlife populations, trafficking methods, and conservation strategies to inform policy and action.
References
- Down to Earth | illegal online trade of wildlife
- Global Environment Facility | Illegal wildlife trade

