Why in news?
Donald Trump's inauguration as US President is a significant event in American political history and global geopolitics, especially in the Indo-Pacific region.
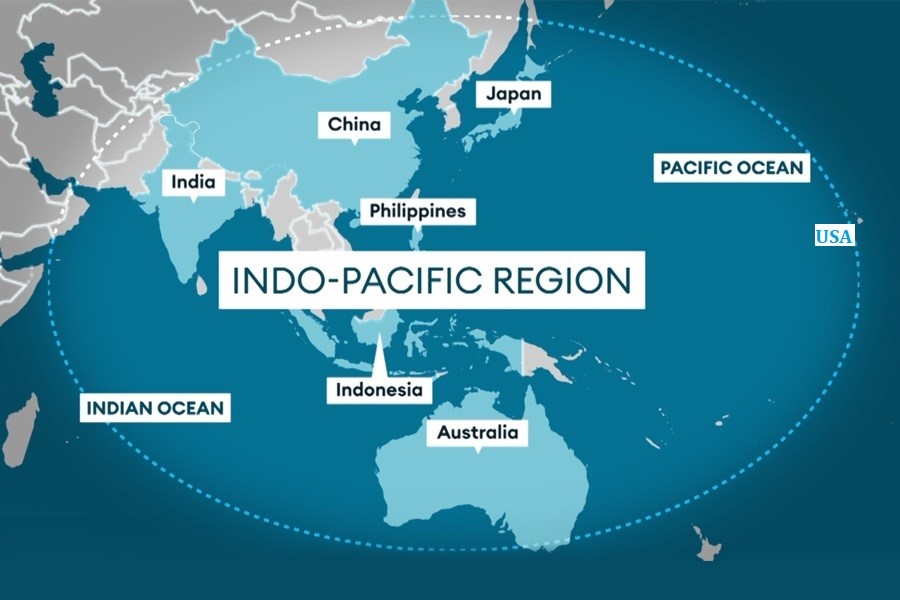
What is Indo-Pacific region?
- The Indo-Pacific region is a geostrategic area encompassing the Indian and Pacific Oceans, bordering countries, East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, and parts of Oceania, including key regions.
Indo-Pacific Nations Overview
- East Asia - China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan
- Southeast Asia - Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines.
- South Asia- India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh.
- Oceania - Australia, New Zealand, Pacific Island nations.
- Other Stakeholders -US, European nations for strategic interests.
What are the significance of the Indo-Pacific Region?
- Hosts world's largest economies- China, India, and Japan. Contains vital global trade routes like the South China Sea and Strait of Malacca.
- Rich in natural resources - Fisheries, energy reserves, and minerals.
- Strategic Importance - Center of power competition, especially between the U.S. and China. Home to major military flashpoints.
- Focuses on countering security challenges and promoting a free, open, rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- Maritime Security - Priorities include ensuring freedom of navigation and addressing piracy, illegal fishing, and environmental threats.
- Technological and Political Dynamics - Hub for technological innovation and infrastructure development.
- Nations often align with U.S. or China in strategic alliances
What are the Major Agreements and Frameworks for the Indo-Pacific?
Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP)
- Origin - Proposed by Japan, adopted by US.
- Core Principles - Promote free, open, rules-based order.
- Commitment to freedom of navigation and overflight in international water.
- Ensures sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Addresses disputes peacefully under international law ( UNCLOS)
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- Launched - In 2022 by the US.
- Involves 14 countries- India, Japan, Australia & Southeast Asia.
- Key Pillars- Trade, Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Energy, Decarbonization, Taxation, Anti-Corruption.
- Aims - To establish modern economic framework without traditional free trade agreement.
Quad Security Dialogue
- Members - US, India, Japan, Australia.
- Aims - To counter China's influence.
- Key focus areas -Maritime security, infrastructure, vaccine production, cybersecurity, critical technologies, climate change.
ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific (AOIP)
- Initiated- By Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
- Focus areas - Maritime, connectivity, sustainable development.
- Aligns- With international laws like UNCLOS.
- Significance - Encourages a central role for ASEAN amid U.S.-China rivalry.
Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements
- AUKUS - A trilateral security pact between Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States, focusing on defense technology, including nuclear-powered submarines.
- India-Japan-Australia Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) - Aimed at reducing dependency on China by diversifying supply chains in critical industries.
What is India's Role in Indo-Pacific Cooperation?
- Participated in Quad - (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) with members from India, U.S., Japan, and Australia.
- Advocates peaceful initiatives - While countering aggressive regional postures.
- Aligns with ASEAN’s Outlook on - The Indo-Pacific (AOIP) for inclusivity and cooperation.
- Secures critical sea- Lanes for global trade and operates Information Fusion Centre (IFC-IOR).
- Collaborates - With Japan, Australia, and U.S. on infrastructure, maritime security, renewable energy, defense ties, and IPEF cooperation.
U.S. Strategy in Indo-Pacific: Key Pillars
- Rules-Based Order - Advocates for freedom of navigation and peaceful dispute resolution under international law.
- Strengthening Alliances -Focuses on security, infrastructure, and emerging technologies.
- Countering China - Opposes militarization of the South China Sea and BRI.
- Economic Engagement - Builds resilient supply chains, clean energy, and fair trade practices through IPEF.
- Security and Defense- Advances defense through AUKUS and increased naval deployments.
- Sustainable Development- Promotes climate adaptation, sustainable energy, and transparent infrastructure projects.
Major Initiatives
- Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) - Ensures transparency and sovereignty through partnerships with Quad nations.
- Blue Dot Network - Certifies sustainable infrastructure with Japan and Australia.
- Malabar Exercises - Naval drills with Quad members for maritime security.
What are the Major Challenges In Indo-Pacific?
- Geopolitical Tensions- China's rise raises territorial disputes, freedom of navigation, and military build-ups. Territorial disputes between China and neighboring countries remain unresolved.
- Security Concerns- Military rivalries, nuclear proliferation ((notably North Korea) and terrorism and extremism.
- Economic Disparities and Competition- Rapidly growing economies and significant poverty. Trade disruptions like the U.S.-China trade war.
- Climate Change - Rising sea levels, extreme weather, and environmental degradation threaten infrastructure and biodiversity.
- Human Rights and Governance- Criticism for human rights violations and ongoing humanitarian crises.
- Regional Cooperation and Multilateralism - Competing alliances like the U.S.-led Quad and China’s SCO increase regional tensions.
- Technology and Cybersecurity -Cybersecurity threats and competition in 5G and AI.
What lies ahead?
- The Indo-Pacific region is crucial for global stability, security, and prosperity.
- Addressing its challenges requires a comprehensive, collaborative approach, including diplomacy, multilateral cooperation, and investment in sustainable development and technology, balancing competing interests and promoting peace and mutual growth.
Reference
The Hindu | Indo U.S Ties
