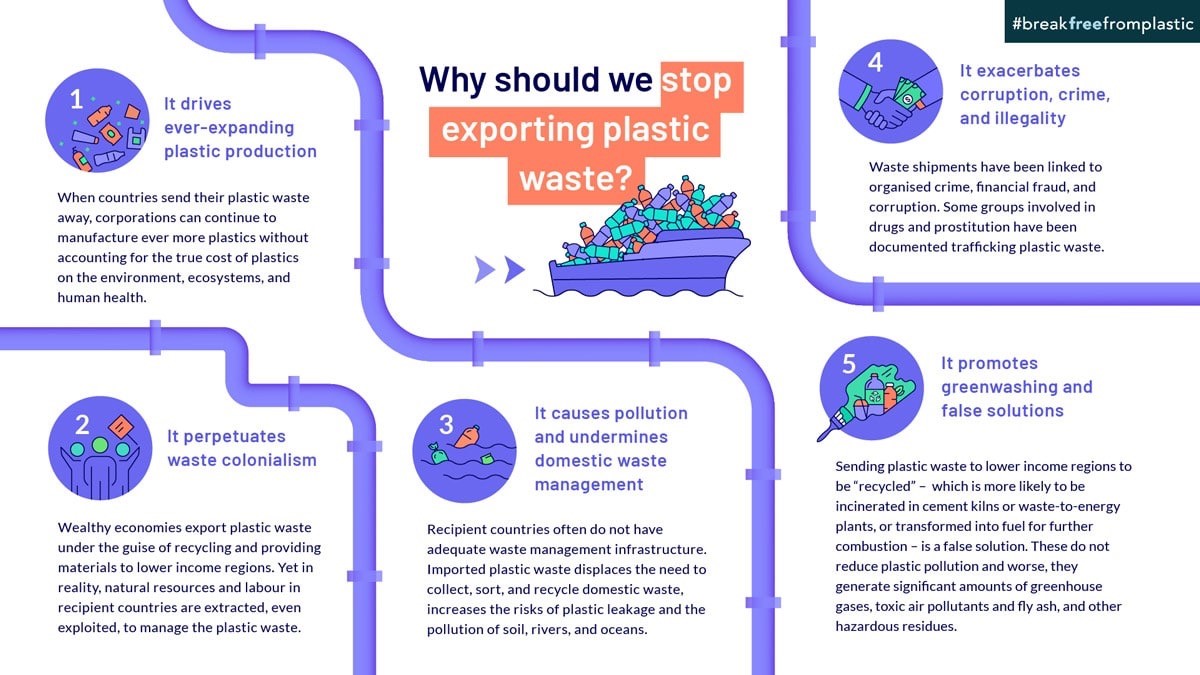
Evidence shows that current recycling practices are insufficient and often counterproductive.
To date, over 10 billion metric tons of plastic have been produced worldwide, with plastic production increasing by more than 18,300% in the past 65 years.
|
Category |
India |
Worldwide |
|
Total Plastic Waste |
Approximately 7.4 million tonnes per year (2024) |
Approximately 220 million tonnes per year. |
|
Plastic Waste Recycled |
Only 8% of its plastic waste |
Only around 9% of all the plastic waste generated globally |
|
Plastic Waste Mismanaged |
68.62% of generated plastics waste is being mismanaged |
Oman tops the list of countries in terms of mismanaged plastic waste. |
|
Single-Use Plastic Ban |
Banned selected 19 single-use plastic items with effect from 2022. |
Bangladesh became the first country to ban thin plastic bags in 2002. |
|
Per Capita Plastic Waste |
15 kilograms per person in 2021. |
Global average is around 28 kg. |
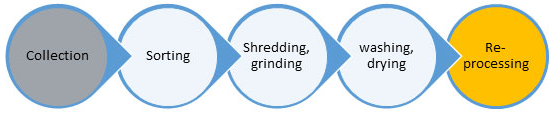
It is estimated that only 9% of all the plastic ever produced has been recycled, with the remaining 91% ending up in landfill or being incinerated.
|
Plastic Waste Trade |
|
|
|
Details |
|
Beginning |
It began in 1988. |
|
Definition |
It is the international trade of waste between countries for further treatment, disposal, or recycling.
|
|
Global Export Statistics |
More than 250 million tonnes have been legally exported across the world. |
|
Impact on Global South |
Shifts the burden of plastic waste to the Global South, often becoming dumping grounds. |
|
Environmental Consequences |
Plastic waste is frequently burned in the open, releasing toxic pollutants and disproportionately affecting vulnerable communities. |
|
Import in India |
India imported around 121,000 metric tons of plastic in 2019, leading to a ban on plastic imports due to environmentalist objections. |
|
Impacts |
Import of plastic waste leads to severe environmental and health impacts, including polluted air and water, increased disease rates, and degraded living conditions. |
|
Environmental Injustice |
Communities near recovery facilities and recycling plants, typically underserved, face increased health risks including polluted air, soil, and drinking water, frequent fires, and exposure to hazardous materials. |