7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
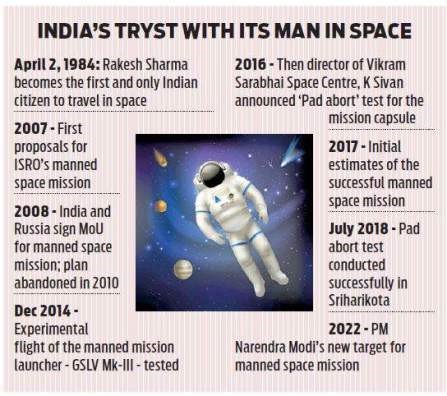
What happened?
What is the significance?
What are the NASA safety guidelines?
How is GSLV in this regard?
What should India do?
Source: Indian Express