7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in news?
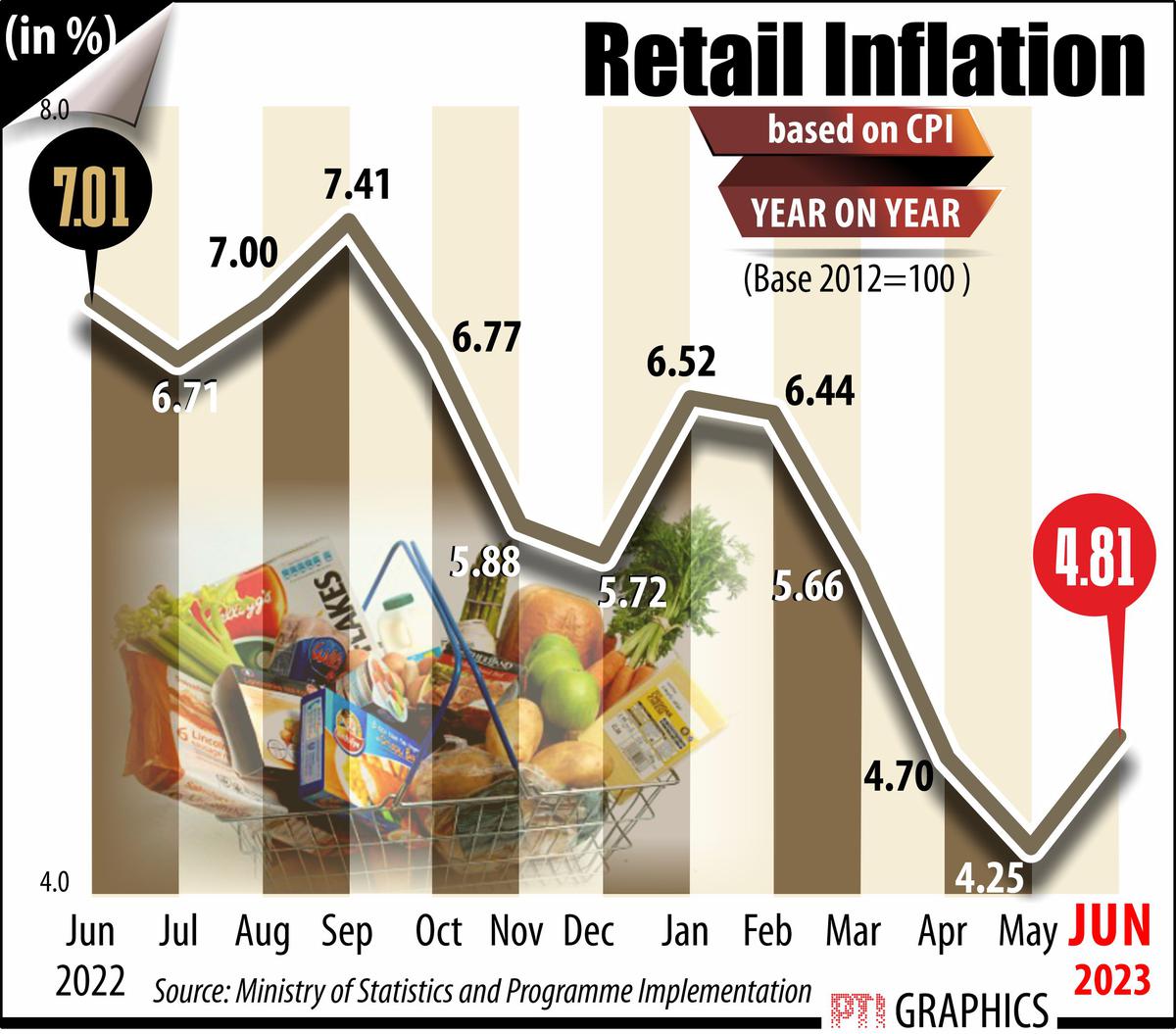
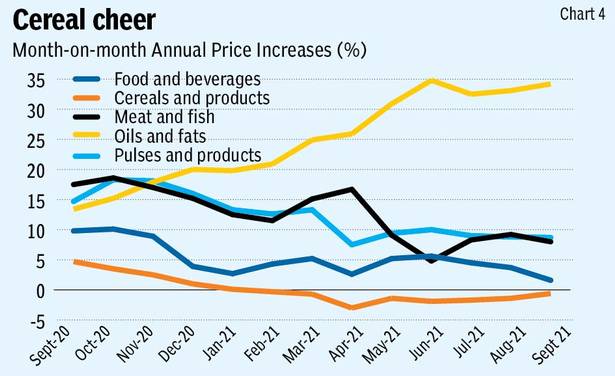
Although Covid-19 infection rates fall and demand revives the world over, the persisting supply chain disruptions could trigger inflationary trends.
Headline inflation is the raw inflation figure reported through CPI that is released monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Core inflation removes the CPI components such as the cost of food and energy that can exhibit large amounts of volatility from month to month and cause unwanted distortion to the headline figure.
Source: The Hindu Businessline