Recently, the Indian Institute for Human Settlements (IIHS) analysed data from 80 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across 24 States between 2012-13 and 2016-17 to understand ULB finance and spending, and found some key trends.
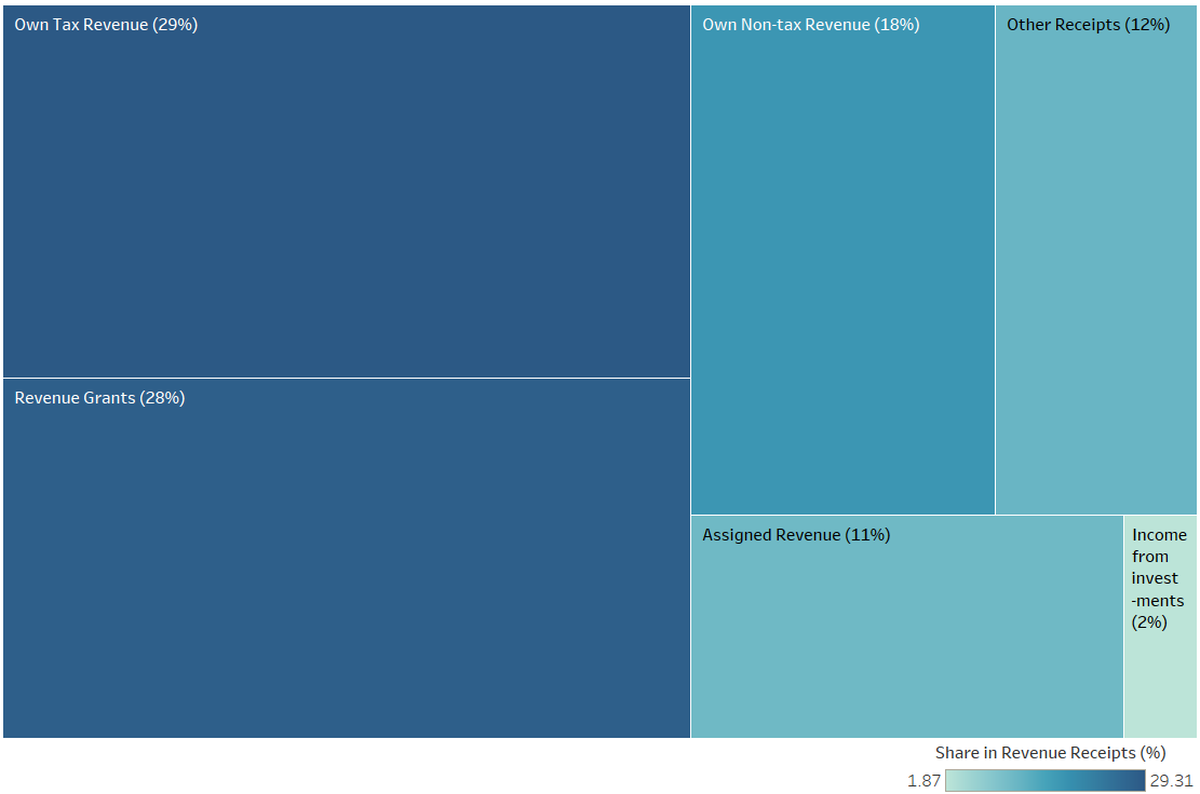
Composition of revenue receipts for the year 2016-2017
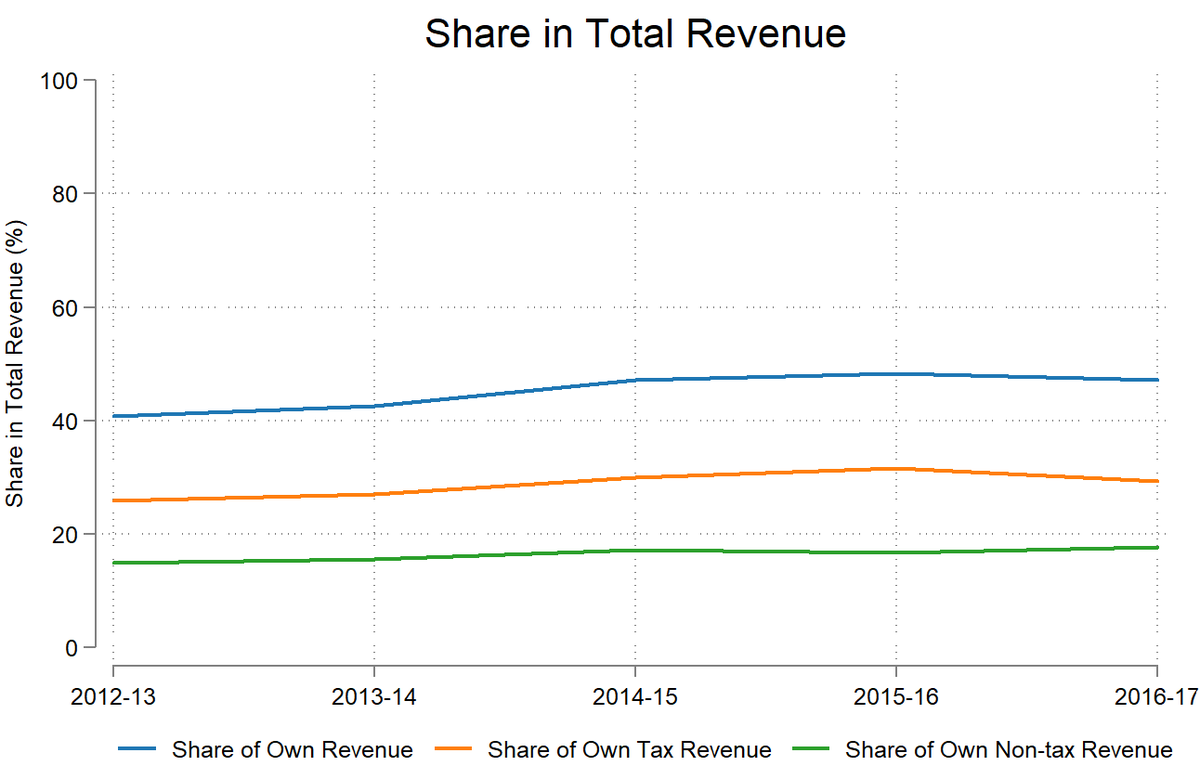
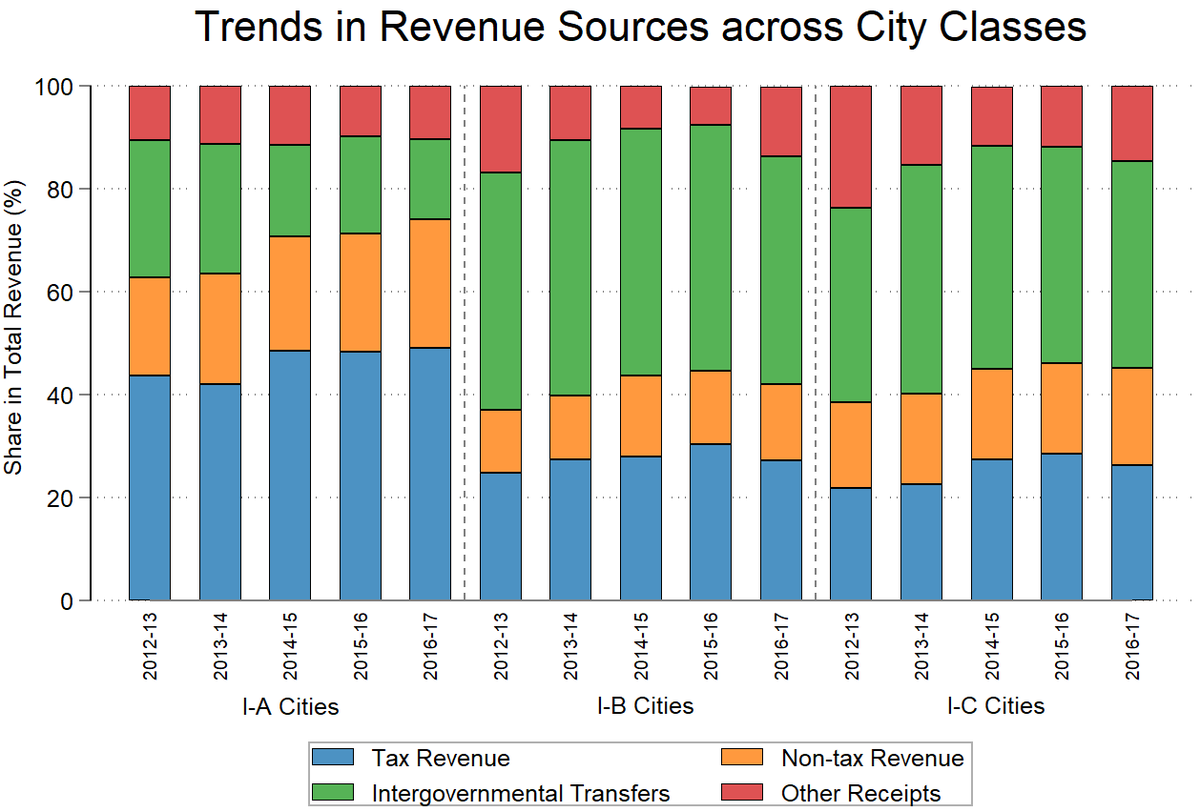
Share in total revenue over the years from 2012-13 to 2016-17
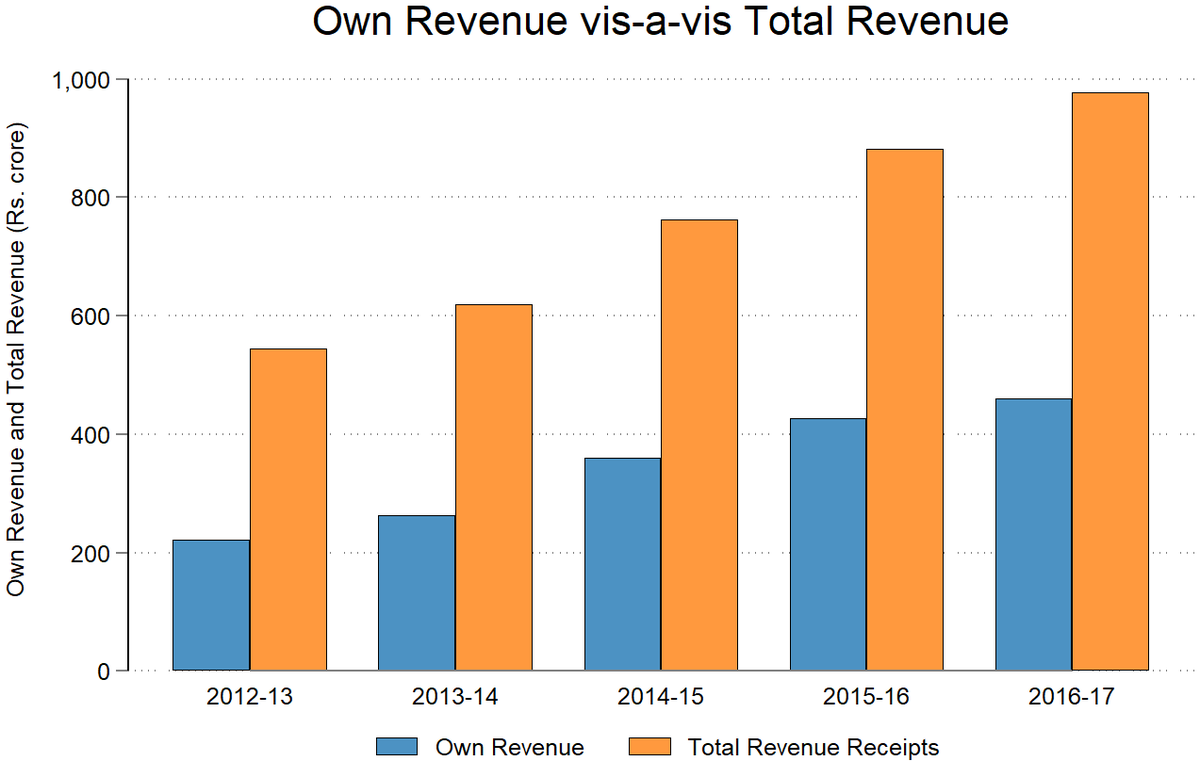
Comparison of own review vs total revenue from 2012-13 to 2016-17
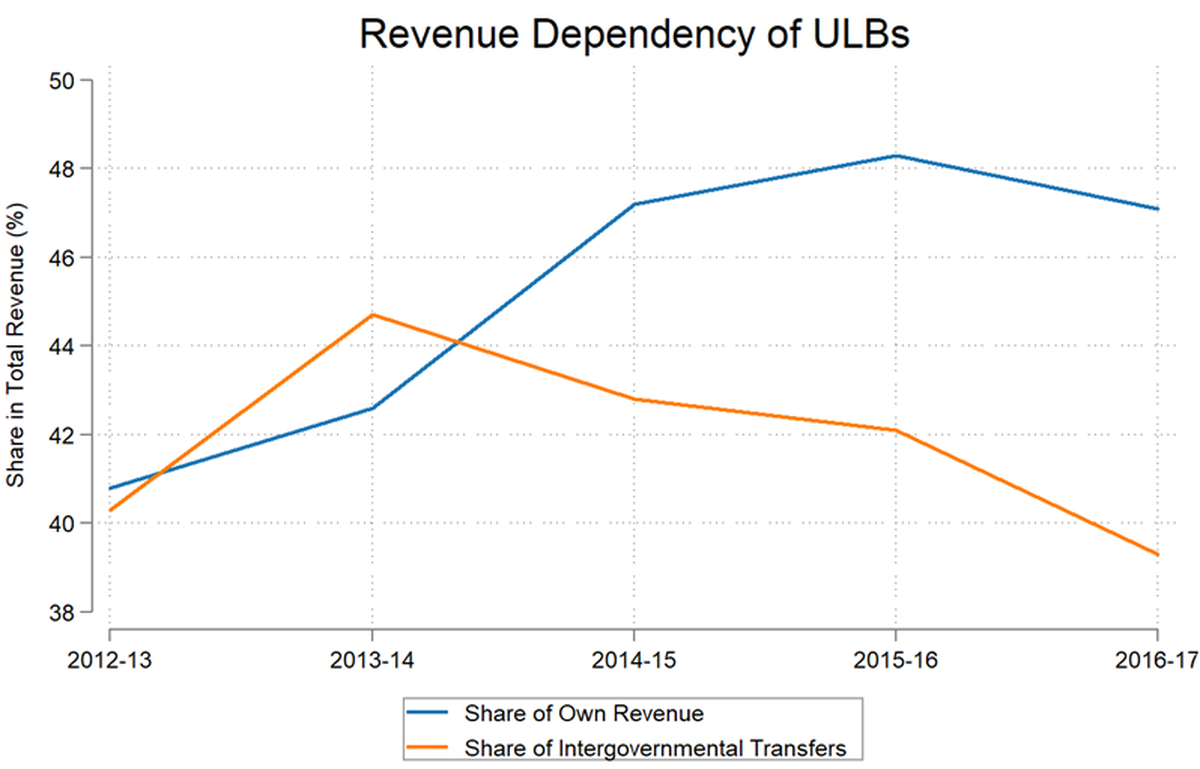
Graph showing the comparison of revenue through IGTs vs Own Revenue
|
City Type |
Dependence |
|
Class I-A cities (population of over 50 lakh) |
Primarily depend on their own tax revenue |
|
Class I-B cities (population of 10 lakh-50 lakh) |
Rely more on IGTs |
|
Class I-C cities (population of 1 lakh-10 lakh) |
Rely more on IGTs |
Reference