7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
The Union Cabinet has recently approved the introduction of the National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill, 2023.
|
Composition of Governing Board |
|
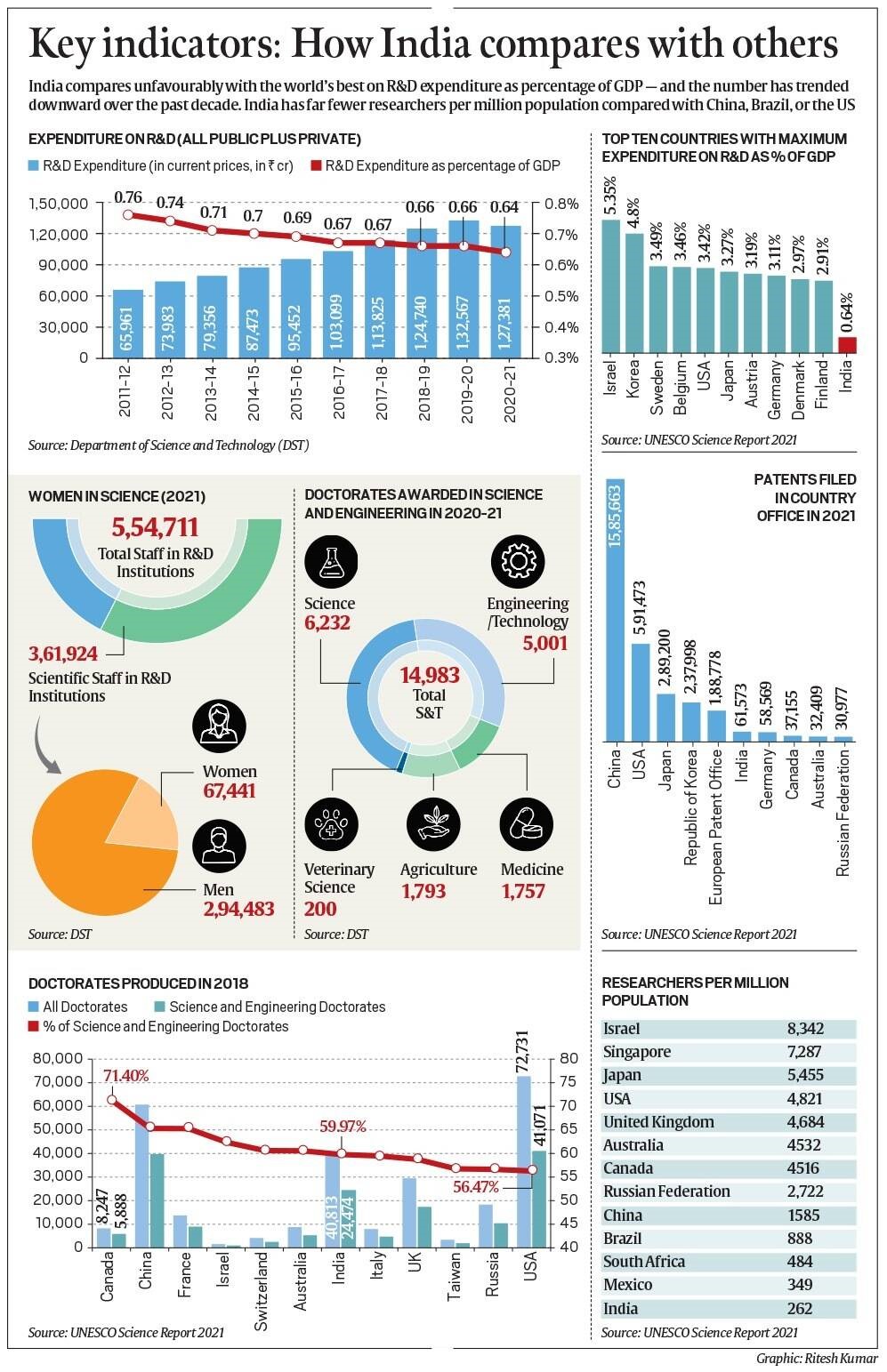
What is the need of the hour?
|
Department of Science and Technology |
|
References