7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
What is the issue?
In Quantitative easing, the central bank purchases longer-term securities from the open market in order to increase the money supply and encourage lending and investment.
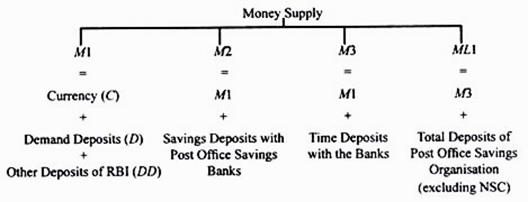
Reserve money = Currency in Circulation + Bankers’ Deposits with RBI + ‘Other’ Deposits with RBI
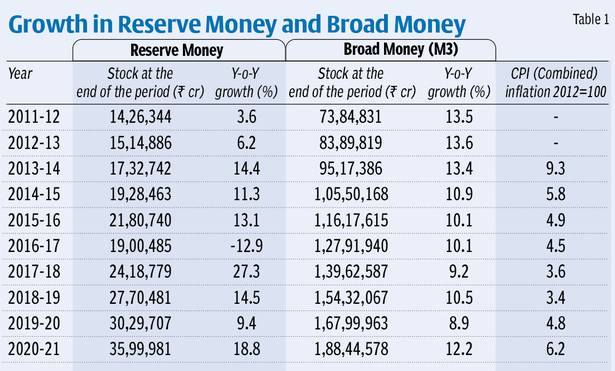
Why inflation targeting has to be looked beyond reserve money growth?
Reference