7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently, Union Budget 2024-25 has proposed removing the 10-12% customs duty on three cancer medicines marketed by AstraZeneca.
|
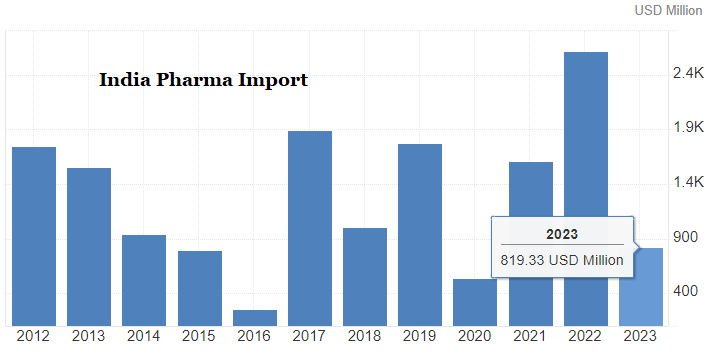
Status of Indian Pharma Industry |
|
Drugs (Prices Control) Order, 2013 (DPCO) is issued under Essential Commodities Act, 1955 by Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
|
|