Under the UN Organisation Stabilisation Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO), the Blue Helmets peacekeepers have thwarted an attack by an armed group in the Congo.
India has been among the largest troop-contributing countries to the UN peacekeeping missions.
In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN Peacekeeping mission.
Reference
Ministry of Defence signed a contract with Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) for supply of ASTRA MK-I Missile for the Indian Air Force (IAF) & Indian Navy under the Buy (Indian-IDDM) category of defence acquisition.
Reference
The scientists have proposed ‘invisible barriers’ in space to explain ‘planes of satellite galaxies’ around the Milky Way and surrounding galaxies.
Reference
Researchers have teleported quantum bits across a rudimentary network, which was done by greatly improving the quantum memory and enhancing the quality of quantum links between the three nodes of the network.
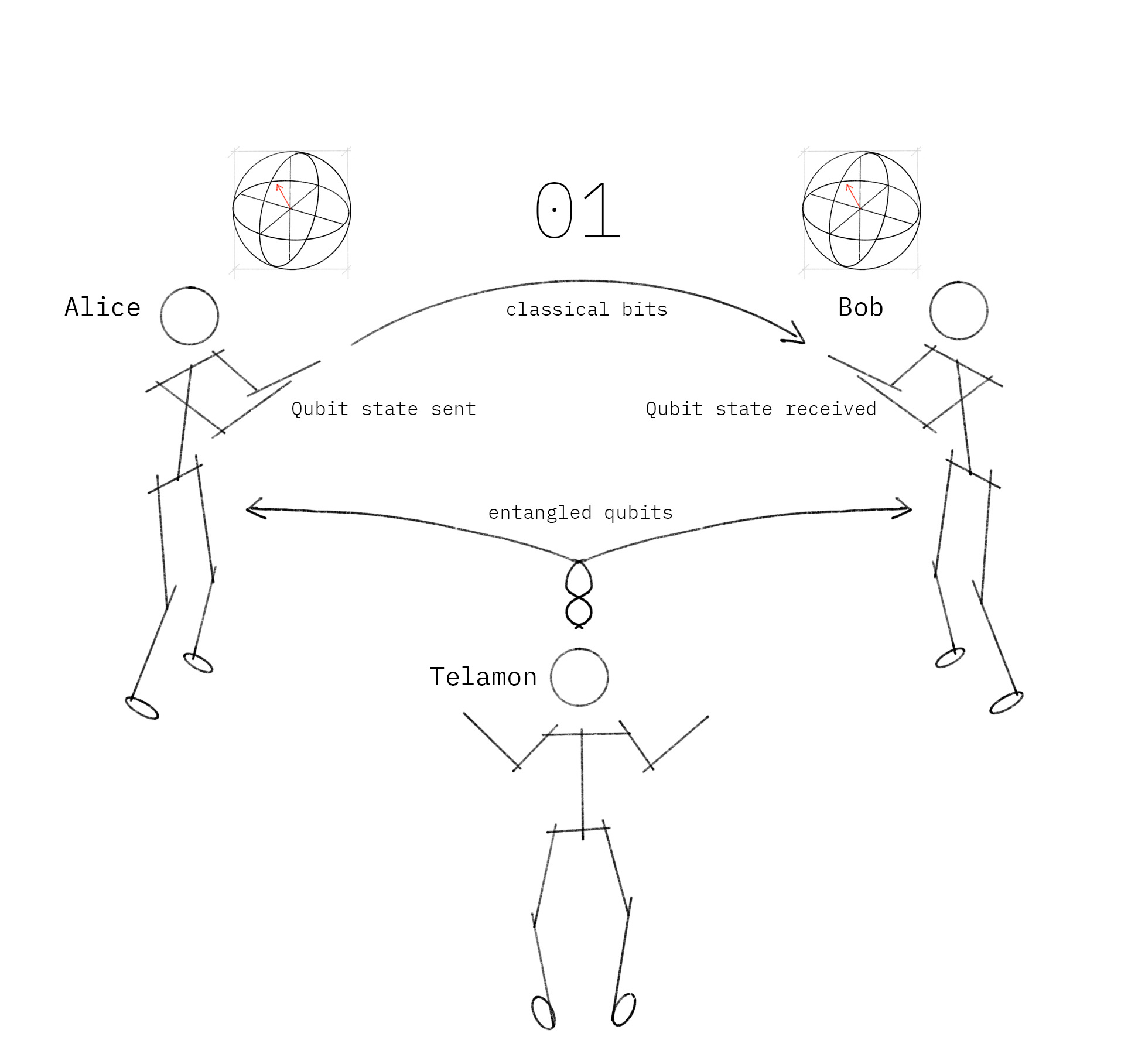
Reference
The Controller General of Accounts (CGA) said that the fiscal deficit has improved to 6.71% of the FY22 GDP over the revised budget estimate of 6.9% mainly on account of higher tax realisation.
Reference