7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
School Education Quality Index
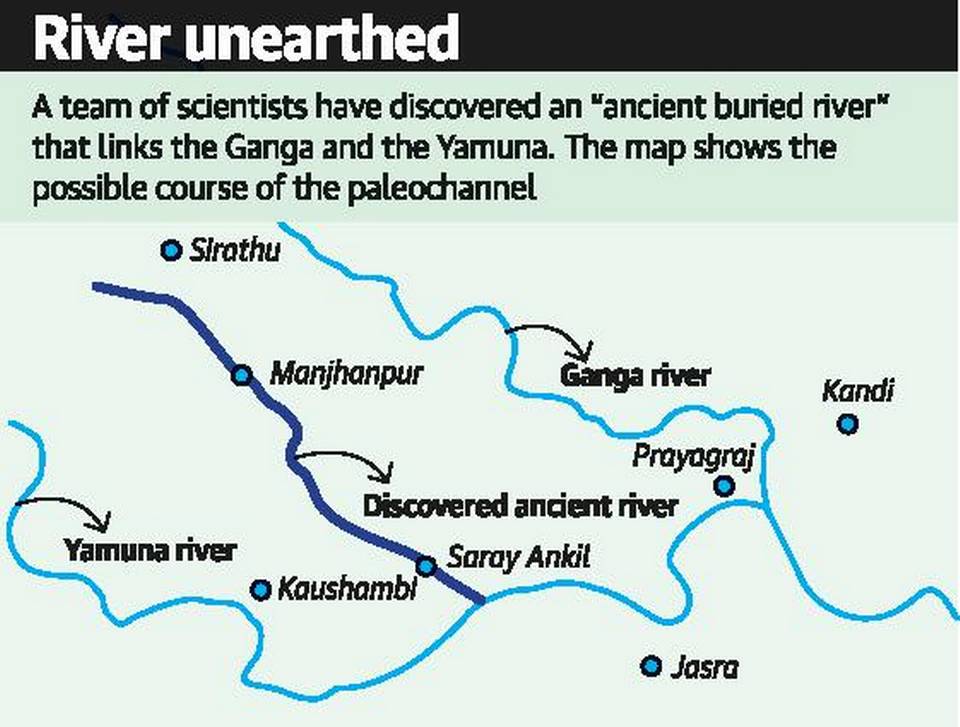
Paleochannel
Apprenticeship Rules
INS Nilgiri
Maitree – 2019
Source: The Hindu, PIB, The Indian Express