7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
RIMPAC
INS Sahyadri
Mission Shaurya
International Organisation for Migration (IOM)
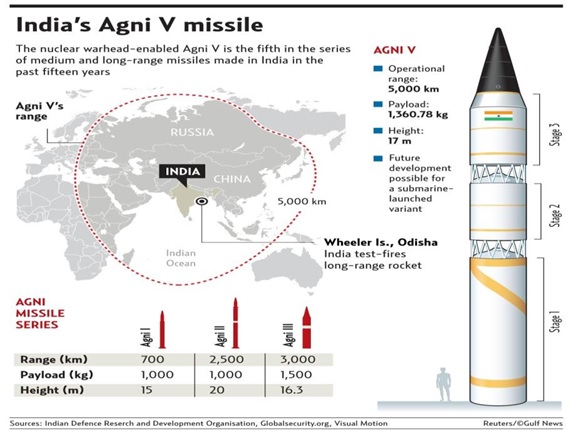
AGNI – V
No-first-use doctrine
Source: The Hindu, Indian Express