7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Coastal Shipping Agreement
Sharavathi Project
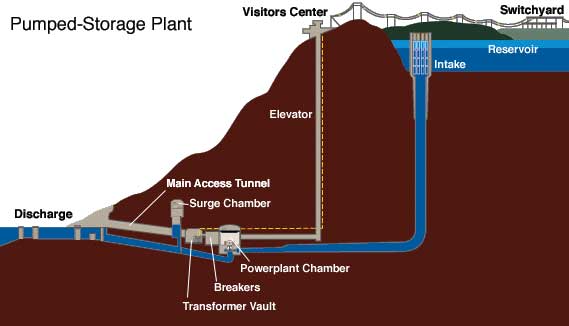
Pumped Storage Scheme
Floating Solar Power Plant
Frequent cyclones in Arabian Sea
Source: The Hindu, PIB, BusinessLine