7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
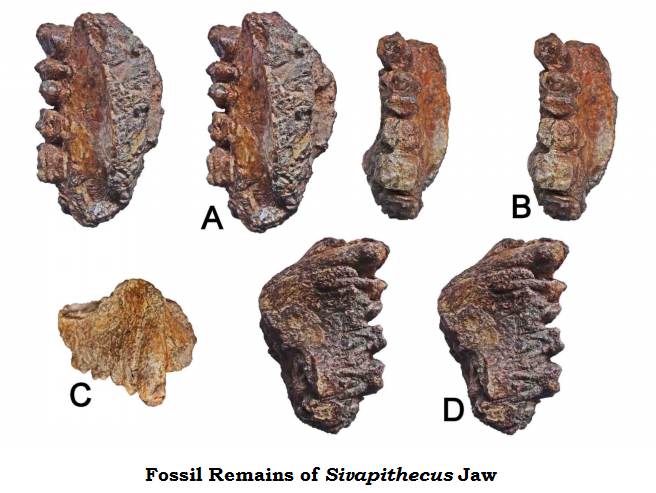
First hominoid ape fossils in Peninsular India
Odisha Skill Development Project
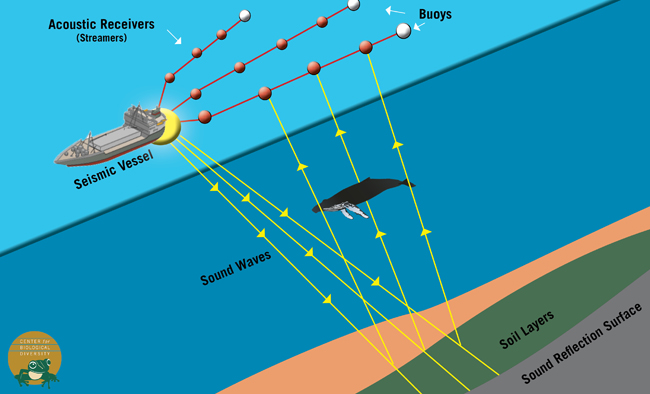
Seismic Airguns & Marine Wildlife
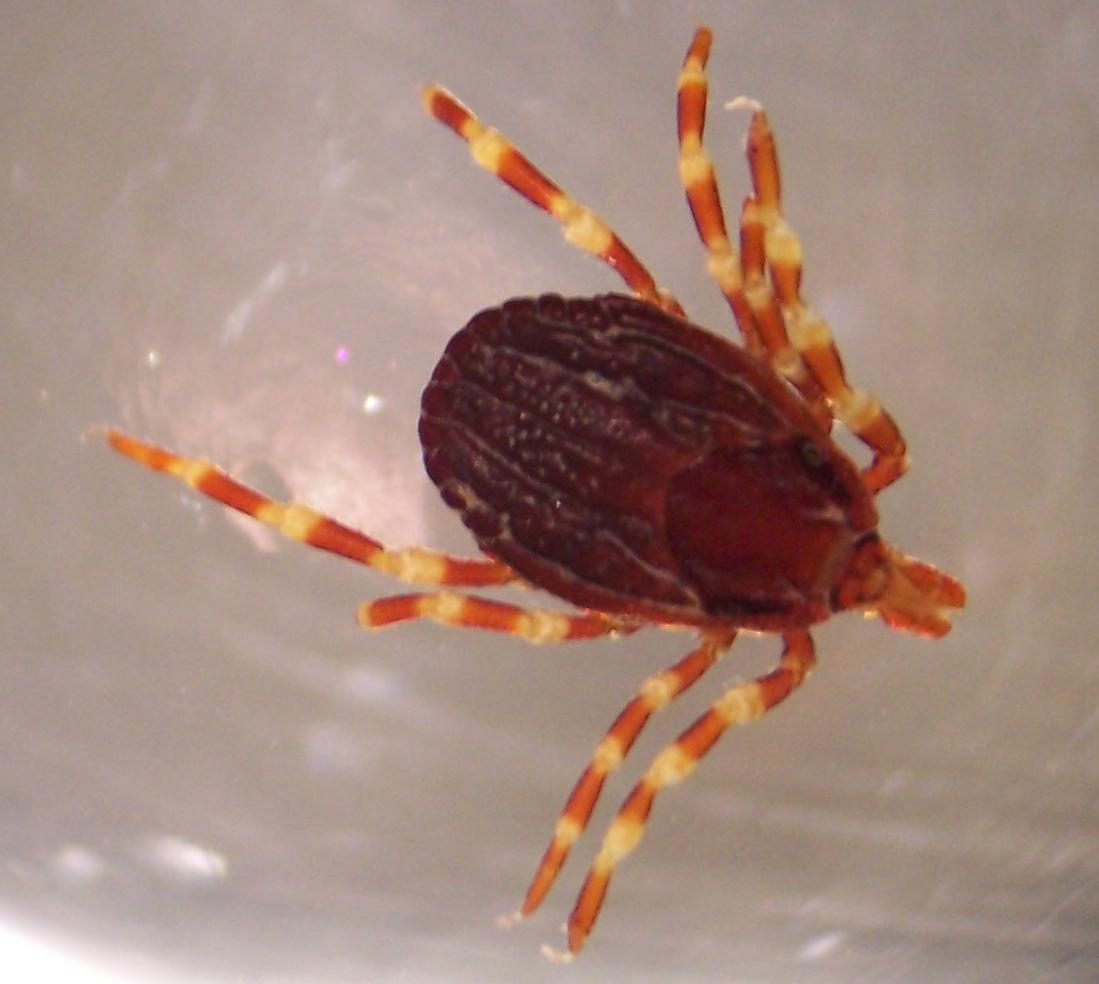
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF)

EX SHINYUU Maitri-2018
Source: PIB, The Hindu