7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
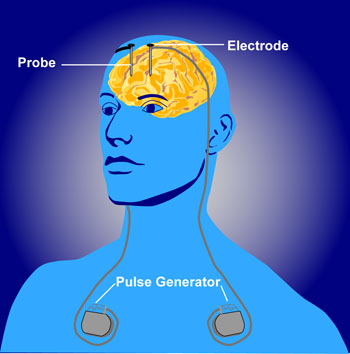
In the US, a patient with severe depression was treated successfully using ‘customised’ deep brain stimulation (DBS) technique for this patient’s case.
DBS is the equivalent of using a pacemaker for the heart.
A proposal has been made to change the name of Corbett National Park to Ramganga National Park.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) approved the Chhattisgarh’s proposal to declare the combined areas of the Guru Ghasidas National Park & Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary as a Tiger Reserve.
Source: The Hindu, The Indian Express