7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Rock nitrogen
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)
National Environment and Engineering Research Institute (NEERI)
e-Office
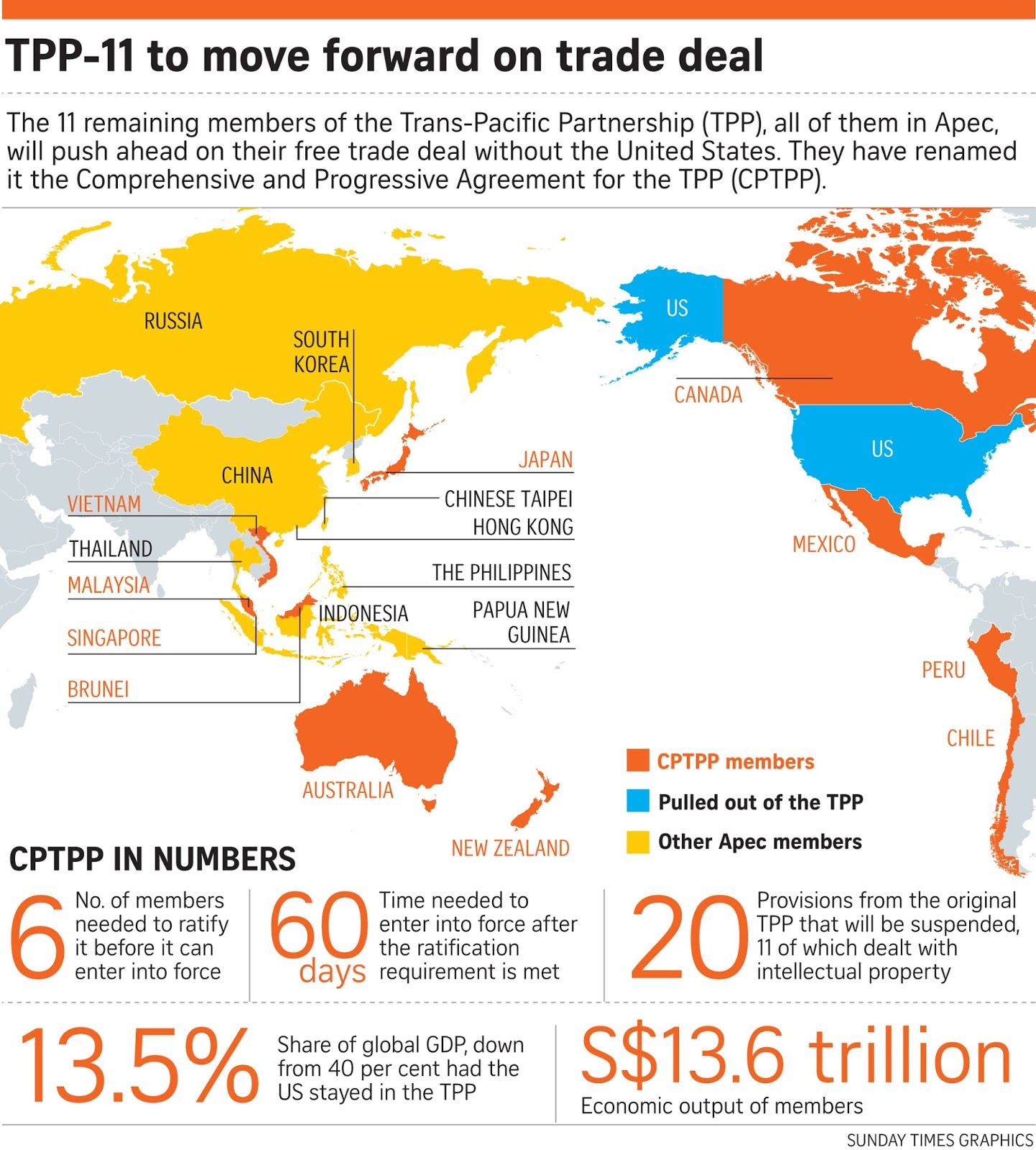
Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
Butterfly fish

Source: PIB, The Hindu