7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS)
Chaukhandi Stupa

Jnanpith Award
Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964
Malaria Detection Chromatography
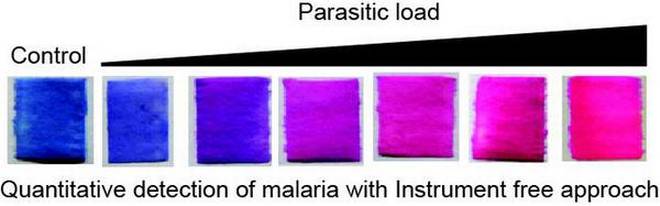
Source: PIB, the Hindu