7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Power to withdraw a case
Protecting heritage along the Hoogly River
Online dashboard to monitor public grievances on real time basis
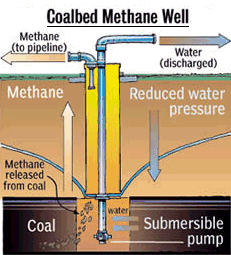
Coal Bed Methane (CBM)
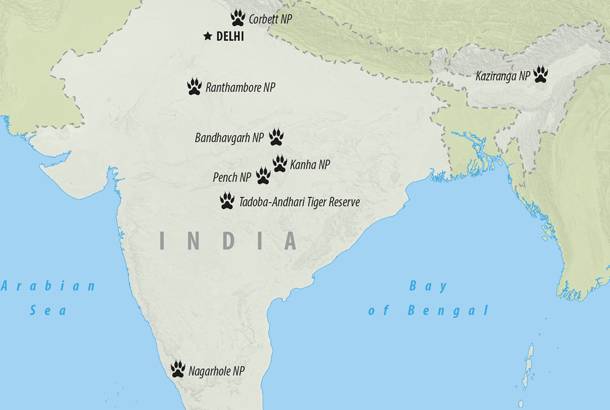
Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve
Pharma waste threatens world’s rivers
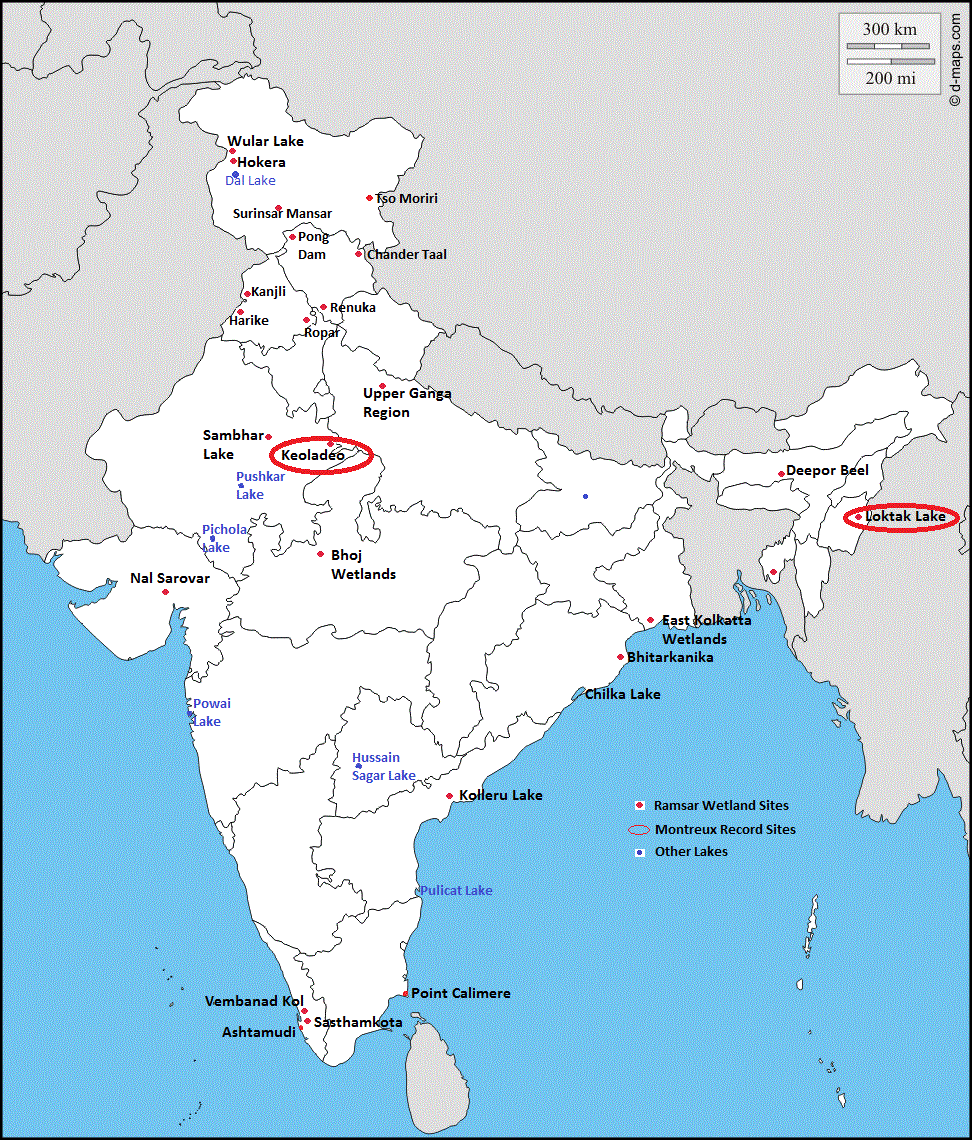
Map of the Day
India Important wetlands
Source: PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express