Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955
Recently, the centre have defended the constitutional validity of Section 6A of Citizenship Act, 1955 before the Supreme Court.
- It is added into the Citizenship Act of 1955 only in 1985.
Citizenship Act, 1955 provides the conditions for getting citizenship by birth, by descent, or by registration. 26th January, 1950 is the cut-off date for establishing citizenship by birth or descent.
- Applicability – Only to Assam.
- Agreement between – The Indian government and the leaders of the Assam Movement.
- Purpose – To preserve and protect the Assamese culture, heritage, linguistic and social identity.
- To furtherance of a Memorandum of Settlement, Assam Accord.
Assam Accord was signed in 1985 between the Union government and the All Assam Students’ Union to determine who is a foreigner in the state of Assam. Clause 5 of the Accord states that 1st January, 1966 shall serve as the base cut-off date for the detection and deletion of ‘foreigners’.
- Cut-off date for citizenship – 1st January, 1966
- Suspended citizenship – This is for illegal migrants from 1st January, 1966 to 25th March, 1971, and who have been found as foreigners, can become full citizens only 10 years from the date of declaration of foreigner status.
- No citizenship – For illegal migrants after 25th March, 1971.
- Challenges – Having a different cut-off date for Indian citizenship in Assam than in the rest of India.
References
- The Indian Express| Centre defends Section 6A of Citizenship Act
- The Hindu| Cut-off date in determining citizenship status
Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC)
One of the Justice of Supreme Court recommended setting up a Truth and Reconciliation Commission to look into alleged violations of human rights in J&K and to recommend measures for reconciliation.
- It is also known as a ‘truth and justice commission’ or simply, a ‘truth commission’.
- It is an official mechanism to acknowledge and reveal the wrongdoings by both state and non-state.
- Aim – To address and resolve the conflicts of the past.
- Definition – According to the Priscilla B. Hayner, a TRC
- Focusses on the past, rather than ongoing events
- Investigates a pattern of events over a period of time
- Engages directly and broadly with the affected population, gathering information on their experiences
- Acts as a temporary body, with the aim of concluding with a final report.
- Is officially authorized or empowered by the state under review
Priscilla B. Hayner authored the book ‘Unspeakable Truths: Transitional Justice and the Challenge of Truth Commissions’ that have the reviews of 40 truth commissions.
- Countries with TRC – Kenya, Uganda, South Africa, Canada, Australia, Sri Lanka and Nepal
- South Africa and Australia are best known and Canada is the most consequential
Truth and Reconciliation Commission focusses on putting together information and evidence from both the victims and the perpetrators of violence, rather than on prosecution and punishment for crimes.
Reference
The Indian Express| Recommendation to set up Truth Commission
Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme
India have launched its 1st Indian Food and Wood certification scheme.
- Launched by – MoEFCC
- Aim – To offer voluntary 3rd party certification to promote sustainable forest management and agroforestry in the country.
- To incentivise entities like State forest departments, individual farmers, or Farmer Producer Organizations, farm forestry and other wood-based industries in the value chain.
- Certification Types
- Forest management (FM) certification
- Tree outside forest management certification
- Chain of custody (CoC) certification
Forest Management certification is based on the Indian Forest Management Standard, an integral part of the National Working Plan Code 2023 which consists of 8 criteria, 69 indicators and 254 verifiers.
- Overseen by – Indian Forest and Wood Certification Council.
- Operating agency – Indian Institute of Forest Management in Bhopal, responsible for overall management.
- The National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies under the Quality Council of India (QCI) will accredit the certification bodies.
- Certification bodies – It will carry out independent audits and assess entities on their adherence to the prescribed standards.
Forest certification seeks to authenticate the origin, legality, and sustainability of forest-based products.

Chain of custody (CoC) certification is meant to guarantee the traceability of a forest product like timber throughout the supply chain from origin to market.
|
Indian Forest and Wood Certification Council
|
- It will act as a multi-stakeholder advisory body.
- Composition – Representatives from Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education, FSI, QCI, IIFM, Union Ministry (Agriculture and Commerce), State Forest Departments, Forest Development Corporations and Wood-based industries
|
References
- PIB| Indian Forest and Wood Certification Scheme
- The Indian Express| Forest certifications
Karan Singh’s Proclamation of 1949
Supreme Court cited Karan Singh’s Proclamation of 1949 while upholding the abrogation of Article 370.
Yuvraj Karan Singh was the heir to the throne of Jammu and Kashmir after his father ‘Maharaja Hari Singh’.
- Repeal of Government of India Act, 1935 – It was until then governed the constitutional relationship between J&K and the dominion of India.
- Applicability of Indian Constitution – It shall govern the constitutional relationship between J&K and Union of India which shall be enforced by the king, his heirs and successors in accordance with the tenor of its provisions.
- Supremacy of Indian Constitution - It shall, as from the date of its commencement, supersede and abrogate all other constitutional provisions inconsistent therewith which were in force in J&K.
- Thus, the paragraph 8 of the Instrument of Accession ceased to be of legal consequence reflecting the full and final surrender of J&K's sovereignty to India.
Instrument of accession (IoA) is an agreement by which the ruler of the princely states agreed to the accession of his kingdom to independent India. Maharaja Hari Singh, then ruler of J&K signed the IoA in 1947.
Article 370 of the Indian Constitution accorded a special status to Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) by substantially limited Parliament’s power to legislate for the State as compared to other States. This was revoked by a Constitution Order of 2019.
Reference
The Indian Express| SC cites Karan Singh’s Proclamation of 1949
Global River Cities Alliance (GRCA)
The GRCA was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference COP28 in Dubai in 2023.
- An India-led initiative inspired by India’s ‘River Cities Alliance’ (RCA).
- Launched by - National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG).
- Secretariat
- NMCG under Jal Shakti Ministry
- NIUA under Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Aim – To empower global efforts towards river conservation and sustainable water management.
- Membership – 9 countries (Indian, Denmark, Cambodia, Japan, Bhutan, Australia, Netherlands, Egypt, and Ghana).
- 142 Indian River cities, river cities of Den Haag from the Netherlands, Adelaide from Australia, and Szolnok of Hungary also joined.
Recently, the RCA had signed a Memorandum of Common Purpose (MoCP) with 124 member Mississippi River Towns and Cities Initiative of the US which is 1st of its kind alliance in the world.
- Supported by – World Bank, Asian Development Bank and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank.
- Activities – Water monitoring program, sharing best practices for renaturing urban areas, and restoring aquatic ecosystems for sustainable urban development initiatives will be discussed.
References
Hindustan Times| Launching of Global River Cities Alliance
|
Other Important News
|
|
EXERCISE “VINBAX-2023”
- It is an annual military training exercise conducted alternatively in India and Vietnam.
- Aim – To foster collaborative partnership, promote inter- operability and share best practices between the two sides.
- The operation is under Chapter VII of United Nations Charter on Peace Keeping Operations.
|
|
TechSaksham Program
- It is a top-up program that uses experiential learning to develop employability skills amongst underserved female students pursuing higher education.
- Introduced by - All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE).
- This program will be delivered in a blended mode - a) instructor led face to face workshops/ classrooms and project work, and b) self-paced online learning modules.
|
|
Universal Dynamic Crosslinker (UDC)
- Researchers at IIT Madras, Columbia University and Colorado State University in the US have developed a technique to merge diverse plastics into strong and recyclable materials.
- A universal dynamic crosslinker (UDC) is a specially designed crosslinker that can blend plastics that are usually incompatible.
- UDCs can be used to compatibilize immiscible mixed plastics.
|
|
‘AMRIT’ (Arsenic and Metal Removal by Indian Technology)
- The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) - Madras has developed a technology called ‘AMRIT’ (Arsenic and Metal Removal by Indian Technology) for the removal of Arsenic and Metal ions from water.
- The technology uses nano-scale iron oxy-hydroxide, which selectively removes arsenic when water is passed through it.
- The technology can also remove other impurities from groundwater, such as Manganese, Uranium, Chromium, Mercury, Fluoride.
|
|
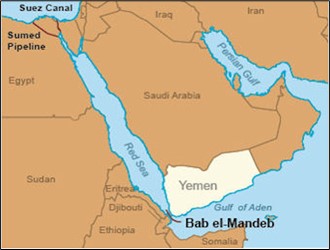
Bab al-Mandab Strait
- It is a strait between Arabia and Africa that connects the Red Sea with the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean.
- The strait is bordered by Yemen on one side and Djibouti and Eritrea on the other.
- It is a strategic route for oil and a chokepoint between the Middle East and the Horn of Africa.
- It's also a vital link in the maritime trade route between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean. About 10% of global trade passes through the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
|
|
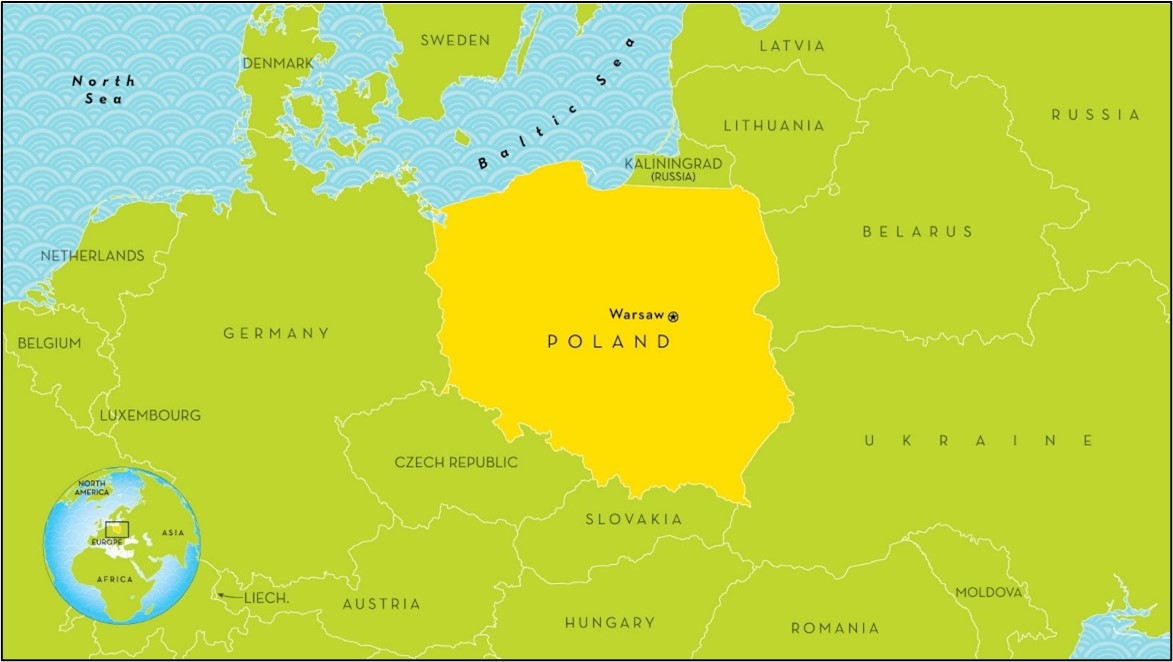
Poland
- Donald Tusk becomes Poland's Prime Minister recently.
- Poland is the 9th Largest Country in Europe. It's bordered by the Baltic Sea to the north.
- The country is bordering
- Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and
- Slovakia to the south,
- Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and
- Lithuania and the Russian enclave of Kaliningrad to the northeast.
|
|
Anthrax
- 5 countries in East and southern Africa are in the middle of outbreaks of the anthrax disease recently.
- It is a serious infectious disease caused by gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- It occurs naturally in soil and commonly affects domestic and wild animals around the world.
- It is a zoonotic disease that can resulting in severe lung problems, difficulty breathing, and shock in humans, usually been found in India’s southern states.
|
|
Pakadwa Vivah
- Pakadwa Vivah is a tradition in Bihar where a boy is kidnapped or coerced and then married to a girl.
- In this practice, the wishes of the boy and girl are not considered.
- The practice is illegal and prevalent in several parts of Bihar.
|
|
AARDO
- The African-Asian Rural Development Organization (AARDO) is an intergovernmental organization that aims to improve rural areas in Asian and African countries.
- It is an autonomous organization established in 1962, headquartered in New Delhi.
- It's one of the earliest examples of South-South cooperation in rural development.
|
|
National Medical Commission
- The new National Medical Commission logo has an image of god Dhanvantri, and replaces the word 'India' with 'Bharat' recently.
- The National Medical Commission (NMC) is India's top regulatory body for medical education and practice.
- It was established in 2020 by the National Medical Commission Act, 2019, replacing the Medical Council of India (MCI).
- The NMC has 33 members.
|
